Discovery could give insight into coronavirus, which has similar features and functions
Credit: Northwestern University
- First study to map atomic structure of a key enzyme complex in paramyxoviruses, a family of RNA viruses
- Enzyme is responsible for assembling RNA molecules, providing a target for new antiviral drugs
- Although from a different family, coronavirus functions similarly
- Researchers used cryo-EM, a revolutionary technique that gives a clear view of proteins
EVANSTON, Ill. — Northwestern University researchers have, for the first time, determined the 3D atomic structure of a key complex in paramyxoviruses, a family of viruses that includes measles, mumps, human parainfluenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
This information could help others design and develop antiviral drugs for these viruses as well as for coronavirus, which functions similarly to paramyxoviruses.
“This takes some of the guesswork out of designing drugs,” said Northwestern’s Robert Lamb, who co-led the study. “Traditionally, you have to develop drugs randomly and hope you hit a target, but it doesn’t happen very often.”
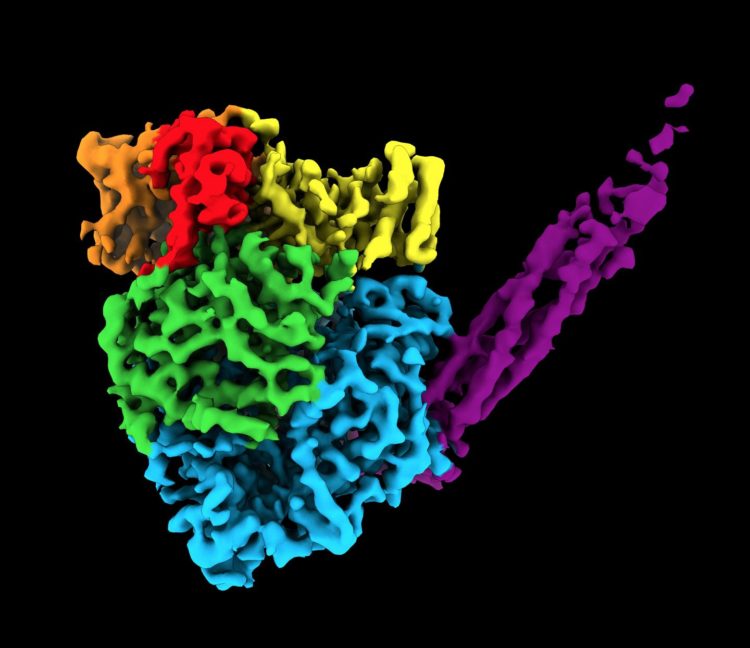
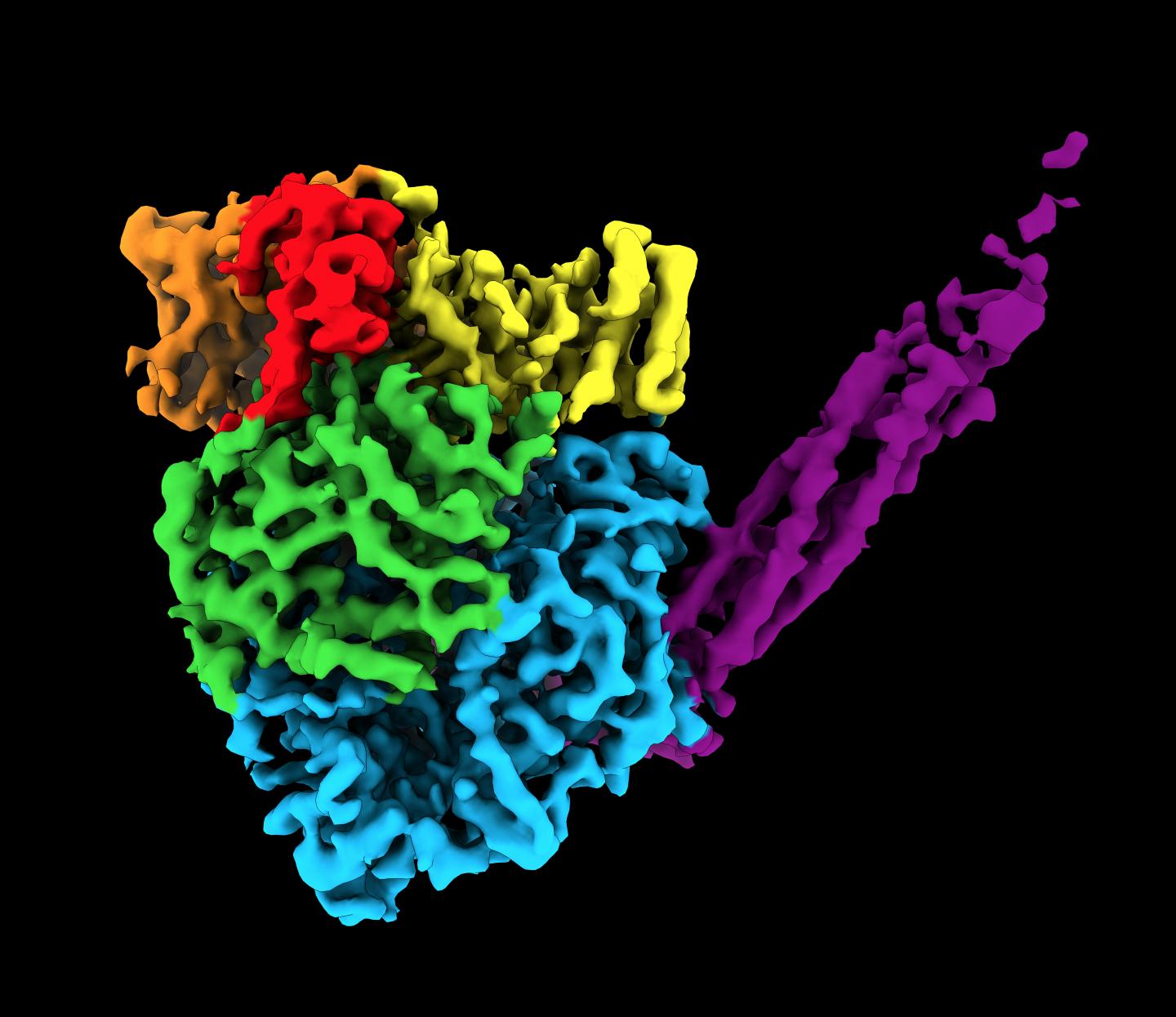
To find the unique structure, researchers used cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM). The relatively new technique enables researchers to peer inside molecules to determine the 3D shape of proteins, which are often thousands of times smaller than the width of a human hair. Before cryo-EM, researchers mainly used X-ray crystallography, which is incapable of capturing high-resolution images of this enzyme. Called a polymerase, the enzyme assembles RNA molecules.
“Crystallography only works for very orderly and organized proteins,” said Northwestern’s Yuan He, who co-led the study. “Virus polymerase complexes are too big to be crystallized and don’t have uniformity.”
The study will be published on Feb. 17 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Lamb is the Kenneth F. Burgess Professor of Molecular Biosciences in Northwestern’s Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences and an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Yuan He is an assistant professor of molecular biosciences in Weinberg.
Although the first documented case of mumps occurred in the 5th century and measles in the 9th century, researchers did not have the equipment to characterize their atomic structures until relatively recently. A trio of biophysicists received the 2017 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing cryo-EM, which ultimately opened the door for Lamb and He.
Cryo-EM works by blasting a stream of electrons at a flash-frozen sample to take many 2D images. For this study, He and his team captured hundreds of thousands of images of one sample of human parainfluenza virus 5 polymerase. The team then used computational algorithms to reconstruct a 3D image.
The resulting image was an irregular, round-shaped globule with a long tail made of four phosphoproteins (or proteins containing phosphorous). The structure contains more than 2,000 amino acids and five proteins.
“Part of the image was expected,” Lamb said. “But part of it was a surprise. Two of the proteins are completely new. They have never been seen before.”
Another surprise: the team found that this virus uses the same protein to switch between genome replication and transcription.
“This machinery has a dual-function,” He said. “It gets both jobs done with one enzyme. The virus’s genome is so small, and this gives it economy of scale.”
Lamb and He hope this work can help others design and develop new drugs for illnesses such as measles and mumps, which have experienced outbreaks in past years.
“A lot of people don’t want to get vaccinated, and they’re getting the disease,” Lamb said. “And for people who are vaccinated, it still takes three to four weeks for that vaccine to take effect. We need more antiviral drugs so people who get infected can be treated immediately.”
###
The study, “Structure of a paramyxovirus polymerase complex reveals a unique methyltransferase-CTD conformation,” was supported by a Cornew Innovation Award from the Chemistry of Life Processes Institute at Northwestern University, the Chicago Biomedical Consortium, and the National Institutes of Health (award numbers R01-GM135651 and T32-GM008382).
More news at Northwestern Now
Find experts on our Faculty Experts Hub
Follow @NUSources for expert perspectives
Media Contact
Amanda Morris
[email protected]
847-467-6790
Related Journal Article
http://dx.