Credit: RUDN
According to a linguist from RUDN University, the number of COVID-19 cases in a country might be related to the existence of aspirated consonants in its main language of communication. This data can help create more accurate models to describe the spread of COVID-19. The results of the study were published in the Medical Hypotheses journal.
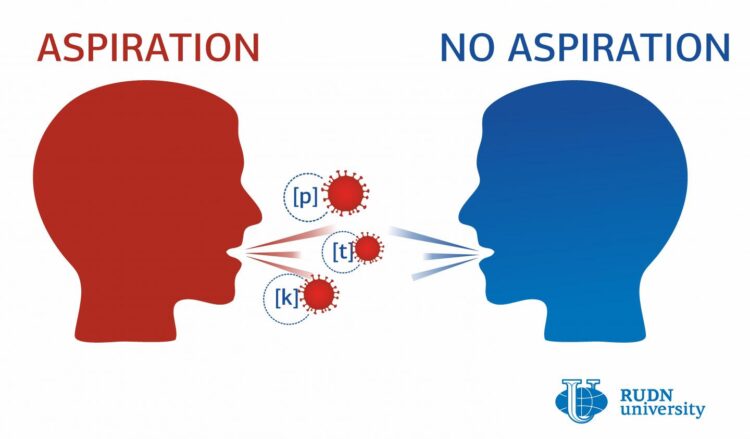
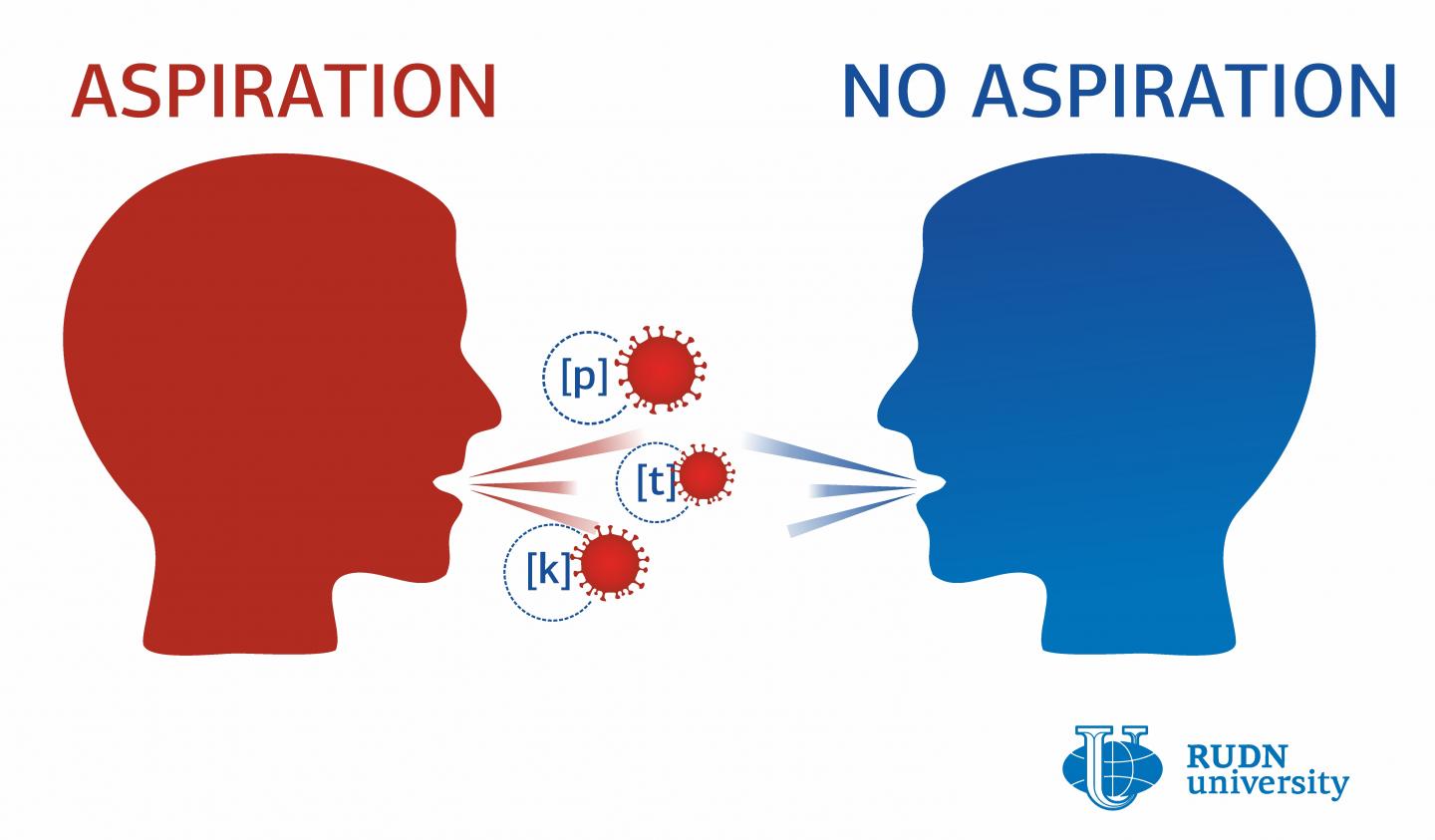
COVID-19 is mainly spread through droplets of liquid coming from the respiratory passages of an infected person. The disease spreads faster through coughing or sneezing, as in these cases the speed of the droplets increases. However, a regular conversation can also lead to infection, and the amount of produced droplets depends on the sounds pronounced by an infected speaker. The exact sounds that add the most to the spread of COVID-19 and other viruses haven’t been identified yet. A RUDN linguist suggested that they might include aspirated consonants, i.e. the sounds that are accompanied by exhalation.
The issue of a correlation between the spread of infections and the language of the infected people was first brought up in 2003, after the outbreak of SARS-CoV-1in South China when over 8,000 cases were registered in 26 countries. The USA accounted for 70 of them, but Japan did not have a single patient, in spite of the fact that the number of Japanese tourists in China at that time was much higher than that of US travelers (3.2 mln vs 2.3 mln, respectively). Some scientists suggested a linguistic explanation: the staff of Chinese stores spoke to US tourists in English, and to Japanese guests in Japanese. Georgios Georgiou from RUDN University found the same correlation for COVID-19.
Unlike in Japanese, in the English language the consonants [p], [t], and [k] are aspirated. When they are pronounced, numerous small droplets are released from the respiratory passages of a speaker into the air. Such droplets may contain viral particles. Japanese has fewer aspirational consonants, and therefore Japanese speakers produce less airborne droplets during a conversation. To confirm whether the speakers of the languages that are rich in aspirated consonants are more prone to the COVID-19 infection, the RUDN linguist used the official data of 26 countries with 1,000+ registered COVID-19 cases as of March 23, 2020.
“Our study did not include Switzerland because it has several official languages. We also excluded countries with too many or too few cases per 1 mln residents (e.g. Italy and Japan, respectively) to avoid extreme values,” said Georgios Georgiou, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the Department of General and Russian Linguistics, Philological Faculty of RUDN University.
The languages in the study were divided into two groups by the presence or absence of aspirated consonants. According to the scientists, although the groups did not show statistically significant differences, the countries that predominantly spoke the languages of the first group had more cases of COVID-19: 255 per 1 million residents (as opposed to 206 cases in the second group).
“Although no clear relationship was observed, we do not rule out that the spread of COVID-19 can be partially due to the presence of aspirated consonants in a country’s main language of communication. This can be a valuable insight for epidemiologists,’ added Georgios Georgiou.
However, the researchers of this paper recognize that it is difficult to determine such a relationship due to experimental limitations. For example, the different social distance measures taken in each country and the fact that we do not know exactly the linguistic background of the speakers in each country, render the paper’s initial assumption just a hypothesis. However, this hypothesis has strong fundaments and can be studied in a future large-scale study.
###
Media Contact
Valeriya Antonova
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.