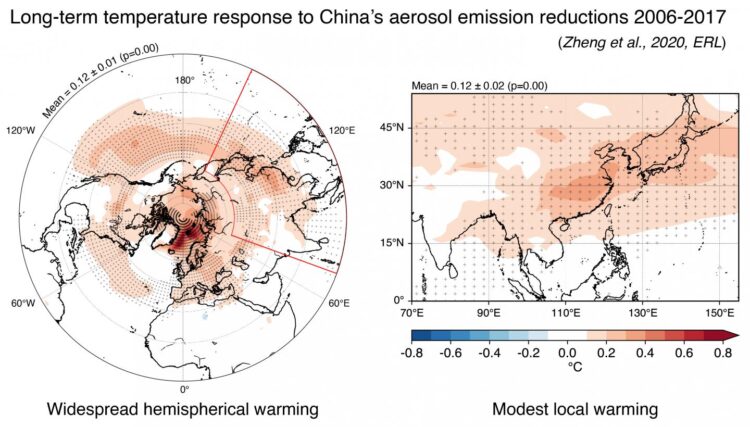
China’s efforts to combat aerosol pollution resulted in warming throughout the northern latitudes
Credit: Yixuan Zheng, Ken Caldeira, Dan Tong,Steven Davis, and Qiang Zhang.
Washington, DC– A 10-year effort by China to improve air quality and reduce pollution-related health risks has caused warming in areas across the northern hemisphere, according to new work published in Environmental Research Letters.
Aerosols are tiny particles that are spewed into the atmosphere by human activities, such as burning coal and wood, or by geological phenomena, like volcanos. Their negative effects on air quality can damage human health and agricultural productivity.
Similar to how the aerosols emitted in a volcanic eruption can cause global temperatures to drop, some aerosols from human activity also have a cooling effect on the climate. Unlike greenhouse gases, which induce global warming by trapping heat in the atmosphere, aerosol particles can cause sunlight to be reflected away from the planet either directly or by interacting with clouds.
“This means that some of the effects of global warming are being masked by aerosol pollution,” explained lead author, Carnegie’s Yixuan Zheng.
Between 2006 and 2017, the Chinese government implemented clean-air policies to reduce the public health risks of aerosol pollutants like sulfate, a cooling agent. These efforts have possibly saved as many as half a million lives a year.
Zheng, along with Carnegie colleague Ken Caldeira, UC Irvine’s Dan Tong and Steven Davis, and Qiang Zhang of Tsinghua University, set out to investigate how these aerosol reductions have affected the global climate.
They applied a sophisticated model based on atmospheric and oceanic systems over a 100-year period, which revealed that China’s pollution-reduction policies might have unmasked about 0.1 degrees Celsius (0.2 degrees Fahrenheit) of greenhouse-gas-induced warming throughout the northern hemisphere–not just in China itself.
“The health risks associated with particulate pollution are very serious and mitigation efforts are unquestionably a good thing,” Caldeira said. “But it’s also important to understand how ongoing and future efforts to improve air quality will create additional challenges in the international fight against climate change.”
###
The Carnegie Institution for Science (carnegiescience.edu) is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.
Media Contact
Ken Caldeira
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.