This article by Dr. Wei Sunf et al. is published in Current Analytical Chemistry, Volume 14 , Issue 5 , 2018
Credit: Wei Sunf and Bentham Science Publishers
Electrochemical sensors and biosensors allow researchers to measure small quantities of chemicals or physico-chemical parameters in experimental settings. This is achieved with the use of sensitive electrodes which can detect small changes in electrical signals. Due to this sensitivity, they have diverse applications in engineering and medicine. Newer versions of sensors offer greater sensitivity and accuracy with the help of nanomaterials incorporated in electrodes used in the sensor.
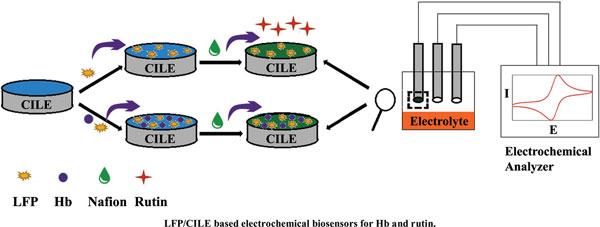
Researchers led by Wei Sun at the College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hainan Normal University have tested electrodes modified with Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) for biochemical analysis or rutin (a citrus flavonoid) and hemoglobin. According to the researchers, LFP is a promising candidate to develop new modified electrodes owing to its advantages such a low cost, environmental compatibility, high safety, non-toxicity, long cycle life and abundance in the environment.
Sun’s team employed scanning electron microscopy to distinguish nanosized LFP particles. The LFP modified electrodes were then prepared by casting the a solution of the particles over the surface of a Carbon Ionic Liquid Electrode (CILE) and adding drops of chitosan on the modified electrodes. Two separate electrodes were prepared for analyzing rutin and hemoglobin, respectively.
The team studied the electrochemical activity of rutin and hemoglobin with these nano-LFP electrodes and achieved detection limits of 8.0 nmol L-1 for rutin and, in the case of hemoglobin, 0.068 mmol L-1 for trichloroacetic acid reduction and 0.07 μmol L-1 for hydrogen peroxide reduction.
###
This article is Open Access. To obtain the article please visit http://www.
Media Contact
Faizan ul Haq
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




