Credit: © 2020 KAUST
A type of anaerobic bacteria responsible for more than 50 percent of nitrogen loss from marine environments has been shown to use solid-state matter present outside their cells for respiration. The finding by KAUST researchers adds to knowledge of the global nitrogen cycle and has important energy-saving potential for wastewater treatment.
Living organisms use oxidation/reduction reactions to harvest the energy they need for survival. This involves the transfer of electrons from an electron donor to an electron acceptor with energy generation. In humans, electrons are released from the food we digest and accepted by soluble oxygen inside our cells. But in many bacteria, other strategies are used for oxidation/reduction, with different types of electron donors and acceptors.
Anammox are anaerobic bacteria found in oxygen-lacking marine and freshwater environments, such as sediments. They derive energy by using ammonium as their electron donor and intracellular soluble nitrite as the acceptor, with the release of nitrogen gas–or so scientists thought.
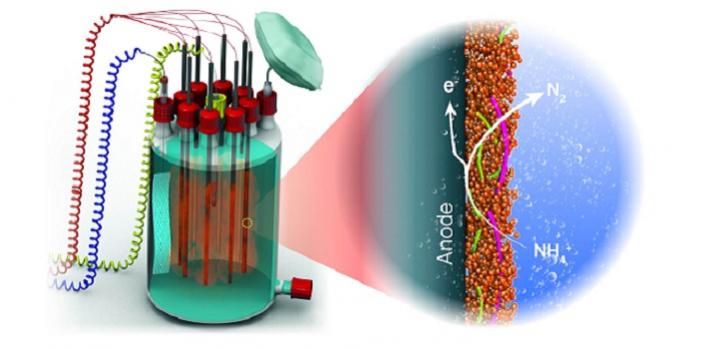
“We found that freshwater and marine anammox bacteria can also transfer electrons from ammonium to extracellular electron acceptors, like graphene oxide or electrodes in microbial electrolysis cells,” says Ph.D. student, Dario Shaw. This novel extracellular electron transfer by anammox bacteria had been conjectured by scientists for more than a decade, but had not been properly explored.
Environmental biotechnologist Pascal Saikaly led a team that found, by looking into the anammox genome, that these bacteria had iron-containing proteins called cytochromes that are also present in types of bacteria known for their ability to transport electrons outside their cells. “We wanted to know if anammox bacteria could also perform extracellular electron transfer,” says Saikaly.
They found that electrons were transferred from ammonium inside the bacteria to solid-state matter outside the cell. For this to happen, the electrons crossed three different barriers, starting from inside an anammox cellular organelle called the anammoxosome. “This means that we have demonstrated for the first time a type of bacteria that can transfer electrons through three different membranes,” says Saikaly. “This finding challenges our perceptions of cell biology.”
“Our findings are a breakthrough in the fields of microbial ecology, bioelectrochemistry and sustainable wastewater treatment,” adds Shaw. Anammox bacteria are already used to make wastewater reusable by removing ammonium. They save energy compared to the conventional use of aerobic bacteria, which require oxygen as the electron acceptor for ammonium oxidation. Providing oxygen through an aeration system requires a lot of energy. Anammox bacteria used for wastewater treatment do not need oxygen, but they do currently need nitrite as the electron acceptor. This is provided by another type of bacteria that needs oxygen, and thus energy, to produce it.
The new finding suggests that anammox alone could be used for ammonium removal, while also producing energy in the form of an electric current or energy-rich hydrogen gas in microbial electrolysis cells.
###
Media Contact
Carolyn Unck
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




