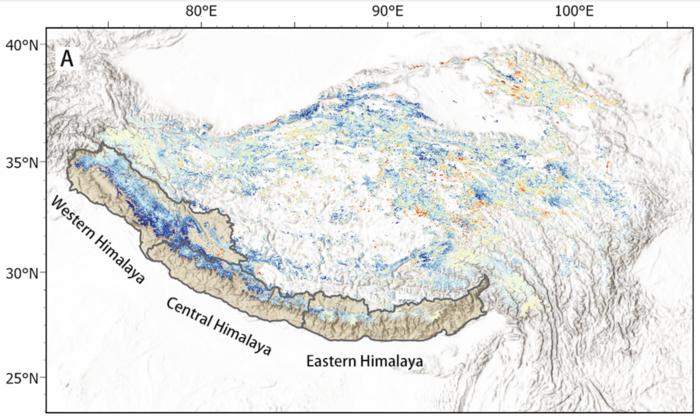
Diminished anthropogenic pollutant emissions during 2020 Covid-19 lockdowns reduced snowmelt in the Himalayas, according to a study. Liqiang Zhang and colleagues used multiple satellite data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI), as well as a coupled atmosphere-chemistry-snow model (GEOS-Chem-SNICAR) to explore how the sudden, dramatic reduction in particulate pollution in the region affected snow and ice melt. Snow and ice on the Tibetan plateau act as a water source for over 20% of the global population. However, ice and snow in the Himalayas have been melting at an accelerating rate in recent decades. While much of this melting is attributable to climate change, air pollution also plays a role, because dark particles of dust and soot that fall on frozen surfaces absorb solar energy and melt the nearby snow and ice. The COVID-19 pandemic created a natural experiment because the Indian national lockdown from 25 March 2020 to 31 May 2020 reduced economic and transportation activities. The authors estimate that the reduced anthropogenic pollutant emissions during the Indian lockdown was responsible for 71.6% of the reduction in radiative forcing on snow in April 2020 compared to the same period in 2019. This reduction in radiative forcing may have prevented 27 Mt in ice and snow melt. The results emphasize the power of reducing anthropogenic pollutant emissions when combating snow and ice melt, according to the authors.
Credit: Hou et al
Diminished anthropogenic pollutant emissions during 2020 Covid-19 lockdowns reduced snowmelt in the Himalayas, according to a study. Liqiang Zhang and colleagues used multiple satellite data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI), as well as a coupled atmosphere-chemistry-snow model (GEOS-Chem-SNICAR) to explore how the sudden, dramatic reduction in particulate pollution in the region affected snow and ice melt. Snow and ice on the Tibetan plateau act as a water source for over 20% of the global population. However, ice and snow in the Himalayas have been melting at an accelerating rate in recent decades. While much of this melting is attributable to climate change, air pollution also plays a role, because dark particles of dust and soot that fall on frozen surfaces absorb solar energy and melt the nearby snow and ice. The COVID-19 pandemic created a natural experiment because the Indian national lockdown from 25 March 2020 to 31 May 2020 reduced economic and transportation activities. The authors estimate that the reduced anthropogenic pollutant emissions during the Indian lockdown was responsible for 71.6% of the reduction in radiative forcing on snow in April 2020 compared to the same period in 2019. This reduction in radiative forcing may have prevented 27 Mt in ice and snow melt. The results emphasize the power of reducing anthropogenic pollutant emissions when combating snow and ice melt, according to the authors.
Journal
PNAS Nexus
DOI
10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad172
Article Title
The COVID-19 lockdown: A unique perspective into heterogeneous impacts of transboundary pollution on snow and ice darkening across the Himalayas
Article Publication Date
27-Jun-2023




