Modeling predicts that loss of cooling effect attributed to sulfate aerosols will increase surface air temperature if air pollution and carbon dioxide are not simultaneously reduced
Credit: Toshihiko Takemura, Kyushu University
As countries around the world race to mitigate global warming by limiting carbon dioxide emissions, an unlikely source could be making climate goals harder to achieve without even deeper cuts in greenhouse gas production: reductions in air pollution.
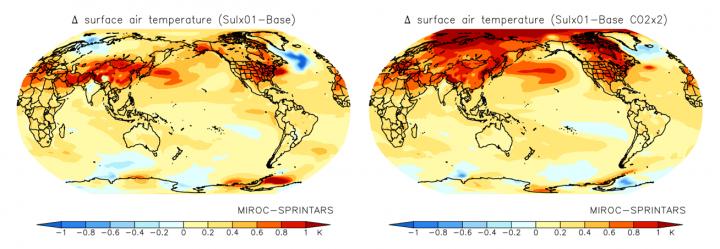
New modeling experiments from Kyushu University in Japan of the long-term effects of reductions in pollutants known as sulfate aerosols predicts further increases in surface air temperature at current and increased carbon dioxide levels because of the loss of an overall cooling effect caused by the light-scattering particles.
“Air pollution causes an estimated seven million premature deaths per year worldwide, so action is essential, especially in emerging and developing countries, which tend to be most affected,” says Toshihiko Takemura, professor at Kyushu University’s Research Institute for Applied Mechanics and author of the study.
“However, reductions in air pollutants must come hand in hand with reductions in greenhouse gases to avoid accelerating global warming.”
To analyze how sulfate aerosols–small particles of sulfur-containing compounds often produced by burning fossil fuels or biomass–influence climate, Takemura used a combination of models known as MIROC-SPRINTARS.
MIROC is a general circulation model taking into account many key aspects of the atmosphere and oceans along with their interactions, while SPRINTARS, which is widely used by news outlets for air pollution forecasts, is capable of predicting the mixing of aerosols in the atmosphere.
Combining the two models allows for effects such as the scattering and absorption of light by aerosols and the interaction of aerosols with clouds to be included in the climate projection.
Looking at the immediate changes to the atmosphere in the case of reduced emission of SO2–a precursor of sulfate aerosols–from fuel sources, Takemura found that changes such as in light scattering and cloud formation by the sulfate aerosols lead to more energy overall entering the atmosphere, though the increase is similar regardless of whether the atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration is the same as present levels or doubled.
However, considering changes in the climate and surface temperatures over longer time scales showed that not only does the surface air temperature increase with a reduction in sulfate aerosols but this increase is even larger when carbon dioxide levels double.
“Although the fast response is similar for both situations, long-term changes caused by more slowly responding factors related to interactions with the oceans and subsequent changes, such as in clouds and precipitation, eventually leads to a bigger temperature increase,” explains Takemura.
“Thus, global warming will accelerate unless increases in greenhouse gas concentrations are suppressed as air pollution control measures decrease sulfate aerosol concentrations, further emphasizing the urgency for reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere,” he concludes.
###
For more information about this research, see “Return to different climate states by reducing sulphate aerosols under future CO2 concentrations,” Toshihiko Takemura, Scientific Reports (2020). https:/
Media Contact
William J. Potscavage Jr.
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




