Credit: KAIST
Can your AI agent judge when to talk to you while you are driving? According to a KAIST research team, their in-vehicle conservation service technology will judge when it is appropriate to contact you to ensure your safety.
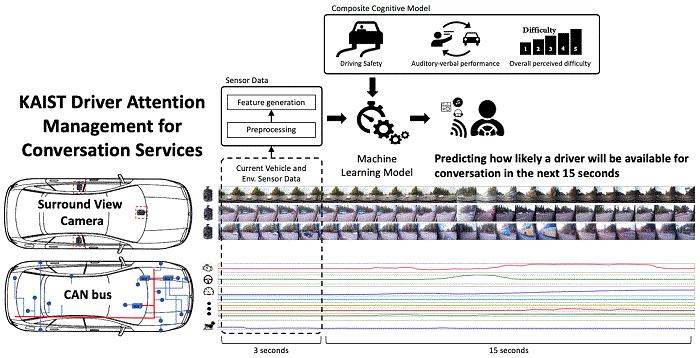
Professor Uichin Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST and his research team have developed AI technology that automatically detects safe moments for AI agents to provide conversation services to drivers.
Their research focuses on solving the potential problems of distraction created by in-vehicle conversation services. If an AI agent talks to a driver at an inopportune moment, such as while making a turn, a car accident will be more likely to occur.
In-vehicle conversation services need to be convenient as well as safe. However, the cognitive burden of multitasking negatively influences the quality of the service. Users tend to be more distracted during certain traffic conditions. To address this long-standing challenge of the in-vehicle conversation services, the team introduced a composite cognitive model that considers both safe driving and auditory-verbal service performance and used a machine-learning model for all collected data.
The combination of these individual measures is able to determine the appropriate moments for conversation and most appropriate types of conversational services. For instance, in the case of delivering simple-context information, such as a weather forecast, driver safety alone would be the most appropriate consideration. Meanwhile, when delivering information that requires a driver response, such as a “Yes” or “No,” the combination of driver safety and auditory-verbal performance should be considered.
The research team developed a prototype of an in-vehicle conversation service based on a navigation app that can be used in real driving environments. The app was also connected to the vehicle to collect in-vehicle OBD-II/CAN data, such as the steering wheel angle and brake pedal position, and mobility and environmental data such as the distance between successive cars and traffic flow.
Using pseudo-conversation services, the research team collected a real-world driving dataset consisting of 1,388 interactions and sensor data from 29 drivers who interacted with AI conversational agents. Machine learning analysis based on the dataset demonstrated that the opportune moments for driver interruption could be correctly inferred with 87% accuracy.
The safety enhancement technology developed by the team is expected to minimize driver distractions caused by in-vehicle conversation services. This technology can be directly applied to current in-vehicle systems that provide conversation services. It can also be extended and applied to the real-time detection of driver distraction problems caused by the use of a smartphone while driving.
Professor Lee said, “In the near future, cars will proactively deliver various in-vehicle conversation services. This technology will certainly help vehicles interact with their drivers safely as it can fairly accurately determine when to provide conversation services using only basic sensor data generated by cars.”
###
The researchers presented their findings at the ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (Ubicomp’19) in London, UK. This research was supported in part by Hyundai NGV and by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
-Profile
Professor Uichin Lee
Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering
KAIST
[email protected]
-About KAIST
KAIST is the first and top science and technology university in Korea. KAIST was established in 1971 by the Korean government to educate scientists and engineers committed to industrialization and economic growth in Korea.
Since then, KAIST and its 61,125 graduates have been the gateway to advanced science and technology, innovation, and entrepreneurship. KAIST has emerged as one of the most innovative universities with more than 12,000 students enrolled in five colleges and seven schools including 1,000 international students from 80 countries.
On the precipice of its 50th anniversary in 2021, KAIST continues to strive to make the world better through the pursuit in education, research, entrepreneurship, and globalization.
Media Contact
Younghye Cho
[email protected]
82-423-502-294
Original Source
https:/




