Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have designed an artificial intelligence system that rapidly identifies stem cells for growing skin grafts
Tokyo, Japan – Stem cell therapy is at the cutting edge of regenerative medicine, but until now researchers and clinicians have had to painstakingly evaluate stem cell quality by looking at each cell individually under a microscope. Now, researchers from Japan have found a way to speed up this process, using the power of artificial intelligence (AI).
In a study published in February in Stem Cells, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) reported that their AI system, called DeepACT, can identify healthy, productive skin stem cells with the same accuracy that a human can.
Stem cells are able to develop into several different kinds of mature cells, which means they can be used to grow new tissues in cases of injury or disease. Keratinocyte (skin) stem cells are used to treat inherited skin diseases and to grow sheets of skin that is used to repair large burns.
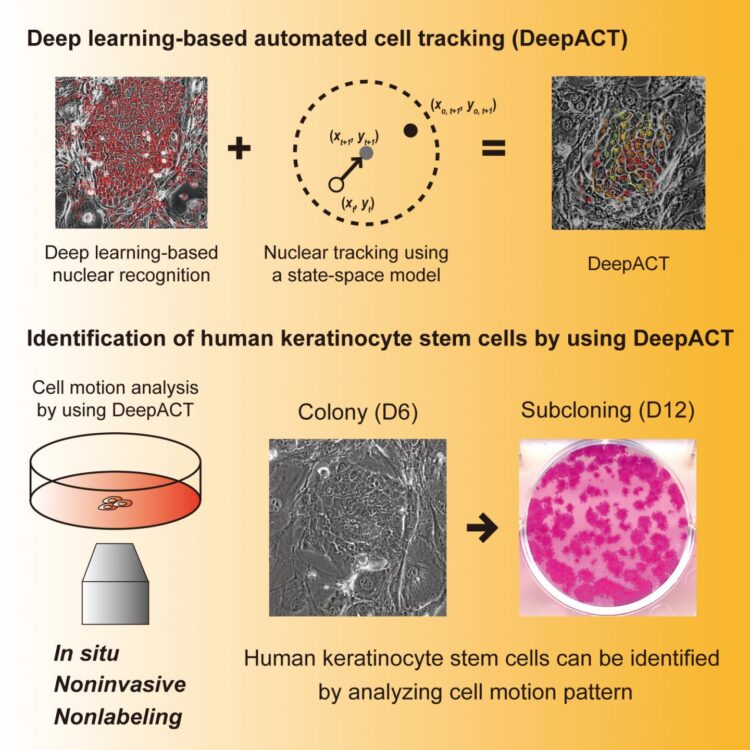
“Keratinocyte stem cells are one of the few types of adult stem cells that grow well in the lab. The healthiest keratinocytes move more quickly than less healthy cells, so they can be identified by the eye using a microscope,” explains Takuya Hirose, one of the lead authors of the study. “However, this method is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and error-prone.”
To address this, the researchers aimed to develop a system that would identify and track the movement of these stem cells automatically.
“We trained this system through a process called ‘deep learning’ using a library of sample images,” says the co-lead author, Jun’ichi Kotoku. “Then we tested it on a new group of images and found that the results were very accurate compared with manual analysis.”
In addition to detecting individual stem cells, the DeepACT system also calculates the ‘motion index’ of each colony, which indicates how fast thecells at the central region of the colony move compared with those at the marginal region. The colonies with the highest motion index were much more likely than the colonies with lower motion index to grow well, making them good candidates for generating sheets of new skin for transplantation to burn patients.
“DeepACT is a powerful new way to perform accurate quality control of human keratinocyte stem cells and will make this process both more reliable and more efficient,” states Daisuke Nanba, senior author.
Given that skin transplants can fail if they contain too many unhealthy or unproductive stem cells, being able to quickly and easily identify the most suitable cells would be a considerable clinical advantage. Automated quality control could also be valuable for industrial stem cell manufacturing, to help ensure a stable cell supply and lower production costs.
###
The article, “Label-free quality control and identification of human keratinocyte stem cells by deep learning-based automated cell tracking,” was published in Stem Cells at DOI: 10.1002/stem.3371.
Media Contact
Daisuke Nanba
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.