Proteins are the building blocks of life, involved in virtually every biological process. Understanding how proteins interact with each other is crucial for deciphering the complexities of cellular functions, and has significant implications for drug development and the treatment of diseases.
Credit: Lupo et al 2024, DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2311887121
Proteins are the building blocks of life, involved in virtually every biological process. Understanding how proteins interact with each other is crucial for deciphering the complexities of cellular functions, and has significant implications for drug development and the treatment of diseases.
However, predicting which proteins bind together has been a challenging aspect of computational biology, primarily due to the vast diversity and complexity of protein structures. But a new study from the group of Anne-Florence Bitbol at EPFL might now change all that.
The team of scientists, including Umberto Lupo, Damiano Sgarbossa and Bitbol, has developed DiffPALM (Differentiable Pairing using Alignment-based Language Models), an AI-based approach that can significantly advance the prediction of interacting protein sequences. The study is published in PNAS.
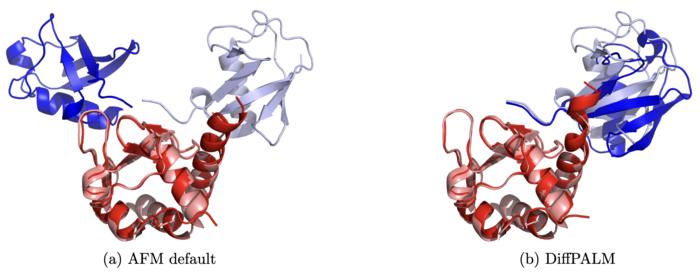
DiffPALM leverages the power of protein language models, an advanced machine learning concept borrowed from natural language processing, to analyze and predict protein interactions among the members of two protein families with unprecedented accuracy. It uses these machine learning techniques to predict interacting protein pairs. This leads to a significant improvement over other methods that often require large, diverse datasets, and struggle with the complexity of eukaryotic protein complexes.
Another advantage of DiffPALM is its versatility, as it can work even with smaller sequence datasets and thus address rare proteins that have few homologs – proteins of different species that share common evolutionary ancestry. It relies on protein language models trained on multiple sequence alignments (MSAs), such as the MSA Transformer and AlphaFold’s EvoFormer module, which allows it to understand and predict the complex interactions between proteins with a high degree of accuracy. Even more, using DiffPALM shows high promise when it comes to predicting the structure of protein complexes, which are intricate structures formed by the binding of multiple proteins, and are essential for many of the cell’s processes.
In the study, the team compared DiffPALM with traditional coevolution-based pairing methods, which study how protein sequences evolve together over time when they interact closely – changes in one protein can lead to changes in its interacting partner. This is an extremely important aspect of molecular and cell biology, which is well-captured by protein language models trained on MSAs. DiffPALM is shown to outperform traditional methods Top of Formon challenging benchmarks, demonstrating its robustness and efficiency.
The application of DiffPALM is obvious in the field of basic protein biology, but extends beyond it, as it has the potential to become a powerful tool in medical research and drug development. For instance, accurately predicting protein interactions can help understand disease mechanisms and develop targeted therapies.
The researchers have made DiffPALM freely available, hoping that the scientific community adopts it widely to further advancements in computational biology and enable researchers to explore the complexities of protein interactions.
By combining advanced machine learning techniques and efficient handling of complex biological data, DiffPALM marks a significant leap forward in computational biology. It not only enhances our understanding of protein interactions but also opens up new avenues in medical research, potentially leading to breakthroughs in disease treatment and drug development.
Reference
Umberto Lupo, Damiano Sgarbossa, Anne-Florence Bitbol. Pairing interacting protein sequences using masked language modeling. PNAS 24 June 2024. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2311887121
Journal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
DOI
10.1073/pnas.2311887121
Article Title
Pairing interacting protein sequences using masked language modeling.
Article Publication Date
24-Jun-2024




