BUFFALO, NY- May 17, 2022 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (Aging-US) Volume 14, Issue 9, entitled, “Single-cell transcriptomics reveals age-resistant maintenance of cell identities, stem cell compartments and differentiation trajectories in long-lived naked mole-rats skin.”
Researchers who authored this research paper are affiliated with the Université Paris Cité, Sorbonne Université, Fondation pour la Recherche en Physiologie, Queen Mary University of London, Hôpital Tenon, Université de Namur ASBL, Ecole Nationale Vétérinaire d’Alfort, and Hôpital Cochin.
“In the present study, we performed extensive in situ analysis and single-cell RNA-sequencing comparing young and older animals.”
Skin acts as an essential barrier and protects organisms from external threats, preventing fluid loss, stabilizing body temperature and relaying sensory information to the brain.
Maintaining skin homeostasis is essential, as alterations in skin functions can cause various deleterious conditions ranging from fluid loss to more severe diseases, such as infections or UV-induced cancers.
Naked mole-rats (NMR) are subterranean rodents characterized by an unusual longevity coupled with an unexplained resistance to aging.
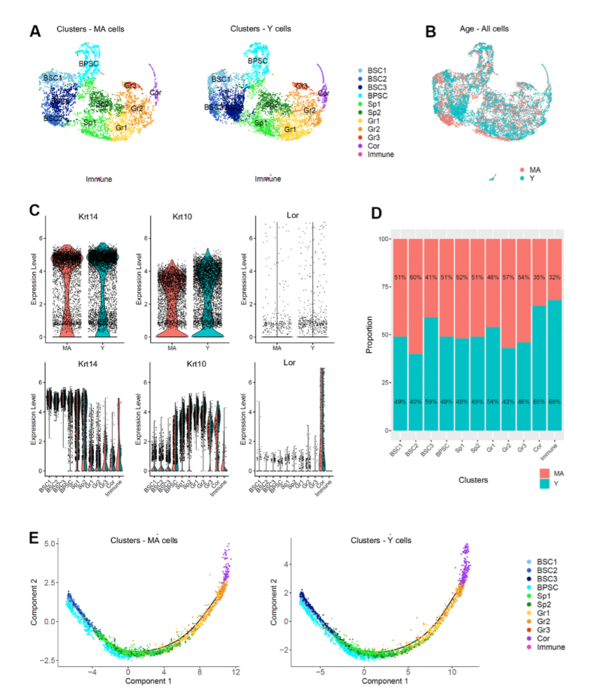
At variance with other species, naked mole-rats exhibited a striking stability of skin compartments and cell types, which remained stable over time without aging-associated changes.
“Thus, we hypothesize that the maintenance of cellular compartments in the older NMR, especially the stem cell pool through high Igfbp3 expression, coupled with an increase skin immunity, could explain their skin slower rate of aging.”
The researchers used single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) to obtain an unbiased molecular RNA profile of the naked mole-rats’ epidermal cell populations. They found that epidermal gene expression did not change with aging. Three classical cellular states defined a unique keratinocyte differentiation trajectory that were not altered after pseudo-temporal reconstruction.
NMR skin healing closure was similar in young and older animals and, remarkably, the number of stem cells was constant throughout aging. The researchers found that NMR epidermal cells displayed two main populations, immune cells (one cluster) and keratinocytes, subdivided into 10 clusters.
“Performing a deeper analysis within each cluster individually, we found 2 genes overexpressed in basal stem cells of older animals and 5 genes overexpressed in immune cells of older animals.”
“Altogether, these results indicate that NMR skin is characterized by peculiar genetic and cellular features, different from those previously demonstrated for mice and humans. The remarkable stability of the aging NMR skin transcriptome likely reflects unaltered homeostasis and resilience.”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204054
Correspondence to: Romain H. Fontaine – Email: [email protected]
Keywords: naked mole-rat, skin stem cells, wound healing, aging
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Follow Aging on social media:
Credit: Aging-US.com
BUFFALO, NY- May 17, 2022 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (Aging-US) Volume 14, Issue 9, entitled, “Single-cell transcriptomics reveals age-resistant maintenance of cell identities, stem cell compartments and differentiation trajectories in long-lived naked mole-rats skin.”
Researchers who authored this research paper are affiliated with the Université Paris Cité, Sorbonne Université, Fondation pour la Recherche en Physiologie, Queen Mary University of London, Hôpital Tenon, Université de Namur ASBL, Ecole Nationale Vétérinaire d’Alfort, and Hôpital Cochin.
“In the present study, we performed extensive in situ analysis and single-cell RNA-sequencing comparing young and older animals.”
Skin acts as an essential barrier and protects organisms from external threats, preventing fluid loss, stabilizing body temperature and relaying sensory information to the brain.
Maintaining skin homeostasis is essential, as alterations in skin functions can cause various deleterious conditions ranging from fluid loss to more severe diseases, such as infections or UV-induced cancers.
Naked mole-rats (NMR) are subterranean rodents characterized by an unusual longevity coupled with an unexplained resistance to aging.
At variance with other species, naked mole-rats exhibited a striking stability of skin compartments and cell types, which remained stable over time without aging-associated changes.
“Thus, we hypothesize that the maintenance of cellular compartments in the older NMR, especially the stem cell pool through high Igfbp3 expression, coupled with an increase skin immunity, could explain their skin slower rate of aging.”
The researchers used single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) to obtain an unbiased molecular RNA profile of the naked mole-rats’ epidermal cell populations. They found that epidermal gene expression did not change with aging. Three classical cellular states defined a unique keratinocyte differentiation trajectory that were not altered after pseudo-temporal reconstruction.
NMR skin healing closure was similar in young and older animals and, remarkably, the number of stem cells was constant throughout aging. The researchers found that NMR epidermal cells displayed two main populations, immune cells (one cluster) and keratinocytes, subdivided into 10 clusters.
“Performing a deeper analysis within each cluster individually, we found 2 genes overexpressed in basal stem cells of older animals and 5 genes overexpressed in immune cells of older animals.”
“Altogether, these results indicate that NMR skin is characterized by peculiar genetic and cellular features, different from those previously demonstrated for mice and humans. The remarkable stability of the aging NMR skin transcriptome likely reflects unaltered homeostasis and resilience.”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204054
Correspondence to: Romain H. Fontaine – Email: [email protected]
Keywords: naked mole-rat, skin stem cells, wound healing, aging
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Follow Aging on social media:
- Twitter – https://twitter.com/AgingJrnl
- Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/AgingUS
- SoundCloud – https://soundcloud.com/aging-us
- YouTube – https://www.youtube.com/agingus
- LinkedIn – https://www.linkedin.com/company/aging
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.204054
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals age-resistant maintenance of cell identities, stem cell compartments and differentiation trajectories in long-lived naked mole-rats skin
Article Publication Date
4-May-2022
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.




