“In this study, we found that DR prevents muscle aging via fbxc-58 in C. elegans.”
Credit: 2023 Hahm et al.
“In this study, we found that DR prevents muscle aging via fbxc-58 in C. elegans.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 25, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed as “Aging (Albany NY)” by MEDLINE/PubMed and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 1, entitled, “The innate immune signaling component FBXC-58 mediates dietary restriction effects on healthy aging in Caenorhabditis elegans.”
Dietary restriction (DR) is a highly effective and reproducible intervention that prolongs longevity in many organisms. The molecular mechanism of action of DR is tightly connected with the immune system; however, the detailed mechanisms and effective downstream factors of immunity that mediate the beneficial effects of DR on aging remain unknown.
In this new study, researchers Jeong-Hoon Hahm, Farida S. Nirmala, Pyeong Geun Choi, Hyo-Deok Seo, Tae Youl Ha, Chang Hwa Jung, and Jiyun Ahn from the Korea Food Research Institute and the University of Science and Technology (in Daejeon, South Korea) investigated the immune signaling that mediates DR effects. The team used Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) to understand the underlying molecular mechanisms of aging and immunity.
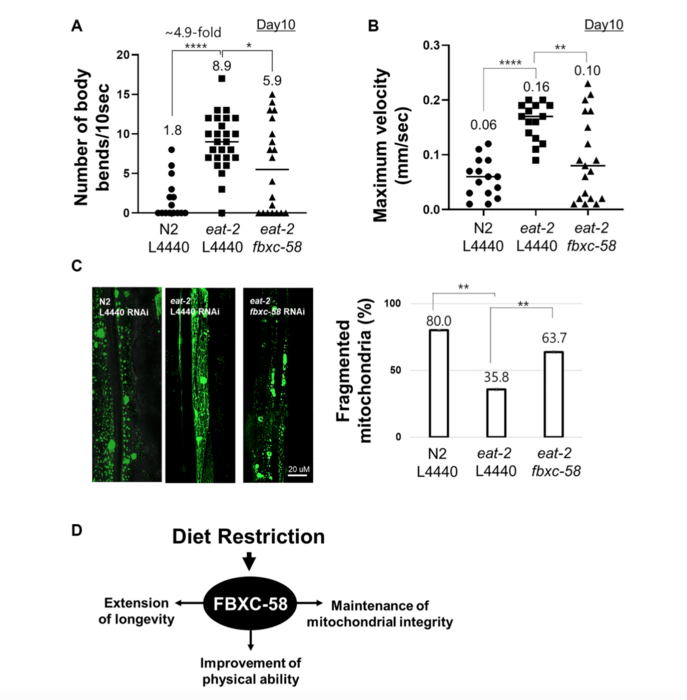
“We found that the F-box gene, fbxc-58, a regulator of the innate immune response, is a novel mediator of DR effects on extending the health span of C. elegans.”
Fbxc-58 is upregulated by DR and is necessary for DR-induced lifespan extension and physical health improvement in C. elegans. Furthermore, through DR, fbxc-58 prevents disintegration of the mitochondrial network in body wall muscle during aging. The researchers found that fbxc-58 is a downstream target of the ZIP-2 and PHA-4 transcription factors, the well-known DR mediator, and fbxc-58 extends longevity in DR through an S6 kinase-dependent pathway. Thus, the team proposed that fbxc-58 may provide a new mechanistic understanding of the effects of DR on healthy aging and elucidate the signaling mechanisms that link immunity and DR effects with aging.
“Thus, we propose that investigating the molecular mechanism of action of F-box proteins, including fbxc-58, in DR will shed light on means to prevent sarcopenia and offer a potentially practical means of encouraging healthy aging via DR.”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204477
Corresponding Authors: Jeong-Hoon Hahm, Jiyun Ahn
Corresponding Emails: [email protected], [email protected]
Keywords: dietary restriction, aging, innate immunity, F-box protein, Caenorhabditis elegans
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204477
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud
- YouTube
- LabTube
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.204477
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
The innate immune signaling component FBXC-58 mediates dietary restriction effects on healthy aging in Caenorhabditis elegans
Article Publication Date
6-Jan-2023




