“In conclusion, the rate of aging can be decelerated by using rapamycin during the early developmental growth phase. This has important theoretical significance but cannot be implemented in humans.”
Credit: 2022 Blagosklonny.
“In conclusion, the rate of aging can be decelerated by using rapamycin during the early developmental growth phase. This has important theoretical significance but cannot be implemented in humans.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 3, 2022 – A new research perspective was published in Aging (listed as “Aging (Albany NY)” by MEDLINE/PubMed and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 14, Issue 20, entitled, “Rapamycin treatment early in life reprograms aging: hyperfunction theory and clinical practice.”
On October 24, 2022, Mikhail Blagosklonny, M.D., Ph.D. from Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center published a riveting research perspective discussing the clinical application of early-life rapamycin treatment and its ability to reprogram aging, based on the hyperfunction theory.
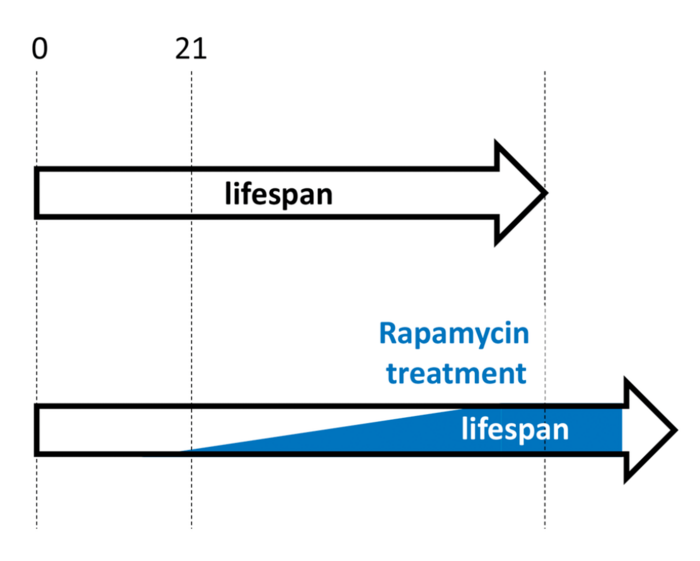
“Making provocative headlines, three outstanding publications demonstrated that early-life treatment with rapamycin, including treatments during developmental growth, extends lifespan in animals, confirming predictions of hyperfunction theory, which views aging as a quasi-program (an unintended continuation of developmental growth) driven in part by mTOR.
Despite their high theoretical importance, clinical applications of two of these studies in mice, Drosophila and Daphnia cannot be implemented in humans because that would require growth retardation started at birth.
A third study demonstrated that a transient (around 20% of total lifespan in Drosophila) treatment with rapamycin early in Drosophila adult life is as effective as lifelong treatment, whereas a late-life treatment is not effective.
However, previous studies in mice demonstrated that a transient late-life treatment is highly effective.
Based on hyperfunction theory, this article attempts to reconcile conflicting results and suggests the optimal treatment strategy to extend human lifespan.”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204354
Corresponding Author: Mikhail V. Blagosklonny – Corresponding Email: [email protected]
Keywords: senescence, gerostatics, geroscience, sirolimus, healthspan
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204354
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud – https://soundcloud.com/Aging-Us
- Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/AgingUS/
- Twitter – https://twitter.com/AgingJrnl
- Instagram – https://www.instagram.com/agingjrnl/
- YouTube – https://www.youtube.com/agingus
- LinkedIn – https://www.linkedin.com/company/aging/
- Reddit – https://www.reddit.com/user/AgingUS
- Pinterest – https://www.pinterest.com/AgingUS/
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.204354
Method of Research
Commentary/editorial
Article Title
Rapamycin treatment early in life reprograms aging: hyperfunction theory and clinical practice
Article Publication Date
24-Oct-2022




