“Therefore, senescent cell eliminators for aging skin cells may be an effective option for treating skin aging.”
Credit: 2022 Takaya et al.
“Therefore, senescent cell eliminators for aging skin cells may be an effective option for treating skin aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 1, 2022 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed as “Aging (Albany NY)” by Medline/PubMed and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 14, Issue 22, entitled, “Glutaminase inhibitors rejuvenate human skin via clearance of senescent cells: a study using a mouse/human chimeric model.”
Skin aging caused by various endogenous and exogenous factors results in structural and functional changes to skin components. However, the role of senescent cells in skin aging has not been clarified.
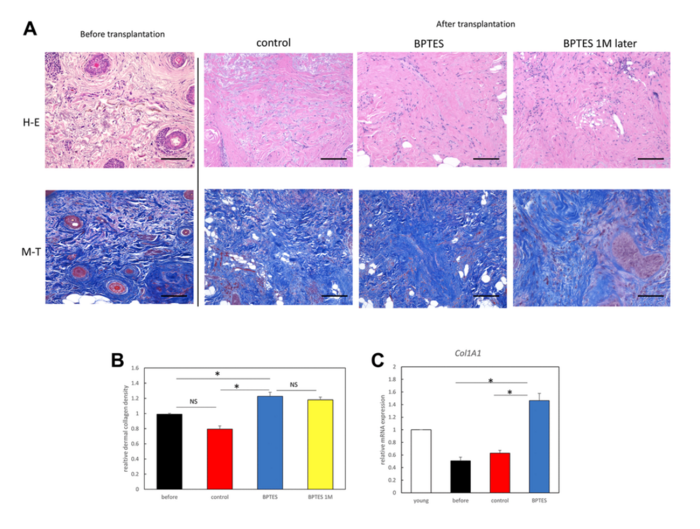
In this new study, researchers Kento Takaya, Tatsuyuki Ishii, Toru Asou, and Kazuo Kishi, from the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at the Keio University School of Medicine, evaluated the effects of the glutaminase inhibitor BPTES (bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1, 3, 4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethyl sulfide) on human senescent dermal fibroblasts and aged human skin to elucidate the function of senescent cells in skin aging.
“[…] we utilized plastic surgery to create an experimental mouse/human chimeric model in which intraoperatively obtained human whole skin layers were transplanted into nude mice using previously described methods [25] and evaluated the anti-aging effects of BPTES on real human skin.”
Primary human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) were induced to senescence by long-term passaging, ionizing radiation, and treatment with doxorubicin, an anticancer drug. Cell viability of HDFs was assessed after BPTES treatment. A mouse/human chimeric model was created by subcutaneously transplanting whole skin grafts from aged humans into nude mice. The model was treated intraperitoneally with BPTES or vehicle for 30 days. Skin samples were collected and subjected to reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), western blotting, and histological analysis.
BPTES selectively eliminated senescent dermal fibroblasts regardless of the method used to induce senescence; aged human skin grafts treated with BPTES exhibited increased collagen density, increased cell proliferation in the dermis, and decreased aging-related secretory phenotypes, such as matrix metalloprotease and interleukin. These effects were maintained in the grafts 1 month after termination of the treatment. In conclusion, selective removal of senescent dermal fibroblasts can improve the skin aging phenotype, indicating that BPTES may be an effective novel therapeutic agent for skin aging.
“In summary, our results indicate that selective clearance of aging dermal fibroblasts by BPTES ameliorates skin senescence-related changes and that aging dermal fibroblasts may play an important role in the skin aging process. Therefore, senescent cell eliminators for aging skin cells may be an effective option for treating skin aging.”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204391
Corresponding Author: Kento Takaya – [email protected]
Keywords: glutaminase inhibitor, human skin, senescent cell, aging, therapeutic agent
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204391
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud – https://soundcloud.com/Aging-Us
- Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/AgingUS/
- Twitter – https://twitter.com/AgingJrnl
- Instagram – https://www.instagram.com/agingjrnl/
- YouTube – https://www.youtube.com/agingus
- LinkedIn – https://www.linkedin.com/company/aging/
- Reddit – https://www.reddit.com/user/AgingUS
- Pinterest – https://www.pinterest.com/AgingUS/
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.204391
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Human tissue samples
Article Title
Glutaminase inhibitors rejuvenate human skin via clearance of senescent cells: a study using a mouse/human chimeric model
Article Publication Date
21-Nov-2022




