“Our findings may provide a useful therapeutic approach for treating breast cancer patients who may suffer from early relapse and intrinsic resistance.”

Credit: 2023 Liu and Wang.
“Our findings may provide a useful therapeutic approach for treating breast cancer patients who may suffer from early relapse and intrinsic resistance.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 16, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 14 on June 12, 2023, entitled, “Are cis-spliced fusion proteins pathological in more aggressive luminal breast cancer?”
A vast majority of breast cancers (~70%) are estrogen receptor-alpha positive (ER+), for which endocrine therapy is the common treatment. However, recurrence often occurs leading to tumor progression, metastasis and eventually patient death, and the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. In this new editorial, researchers Chia-Chia Liu and Xiao-Song Wang from the University of Pittsburgh discuss their recent study regarding recurrent gene fusions — hallmarks of some cancers that resulted either from chromosomal rearrangements or from cis- or trans-splicing.
“Importantly, selected oncogenic fusions have been matched with effective targeted therapy in several solid tumors. For instance, EML4-ALK, one of the most important oncogenic driver genes of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) uncovered in recent years.”
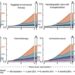
In addition to gene fusions resulting from genomic rearrangements, a read-through SLC45A3-ELK4 fusion transcript has been identified in prostate cancer which is associated with disease progression and metastasis. Although the whole genome and RNA sequencing provide an effective way to detect fusion genes, the downstream identification and validation of fusion genes or their products in solid tumors remains a major challenge. Through analysis of RNA-seq data from TCGA, the authors of this editorial and their co-authors recently identified a neoplastic fusion transcript RAD51AP1-DYRK4 in luminal B breast cancer (~17.5%) showing higher ki67 expression which is an indication of aggressive clinical characteristics.
“In this study, we examined the utility of MEK inhibitor trametinib (Mekinist) currently used for treating melanoma with BRAF mutations, in blocking the MEK-ERK signaling driven by RAD51AP1-DYRK4 fusion. Interestingly […] RAD51AP1-DYRK4 may endow sensitivity to MEK inhibition in luminal B breast cancer [13]. To our knowledge, this is one of the few non-traditional fusions generated by read-through events in the absence of DNA rearrangement that play an important role in tumorigenesis.”
Read the full editorial: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28438
Correspondence to: Xiao-Song Wang
Email: [email protected]
Keywords: luminal B breast cancer, RAD51AP1-DYRK4, MEK inhibitor, chimerical transcript
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
- YouTube
- LabTube
- Soundcloud
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://oncotarget.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Foncotarget.28438
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: [email protected].
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
Journal
Oncotarget
DOI
10.18632/oncotarget.28438
Method of Research
Commentary/editorial
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Are cis-spliced fusion proteins pathological in more aggressive luminal breast cancer?
Article Publication Date
12-Jun-2023