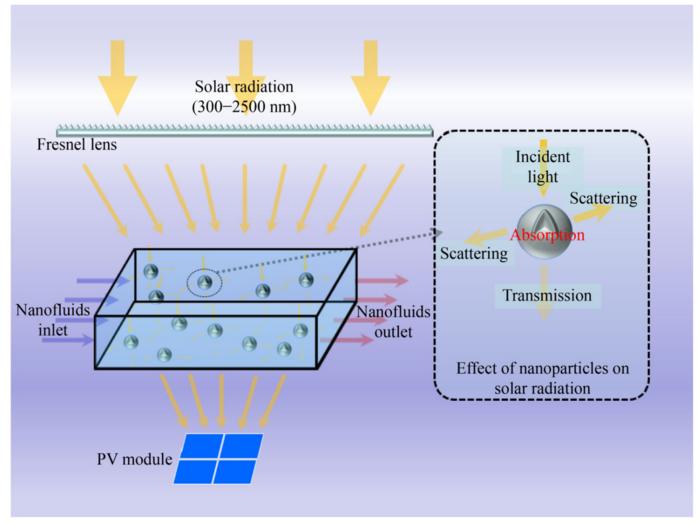
As the globe grapples with the urgent need to shift from fossil fuels to sustainable energy sources, solar power stands as a beacon of hope. However, a significant challenge has been to efficiently capture and utilize the full spectrum of sunlight. Traditional photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight into electricity but can’t use the entire solar spectrum, especially the infrared part which is often wasted as heat. To address this, photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) systems have been developed. These hybrid systems not only generate electricity like PV panels but also capture the wasted heat, providing a dual benefit. The spectral beam splitting (SBS) technology can significantly enhance the collection temperature and system efficiency, and nanofluids commonly serve as splitters in the SBS hybrid PV/T system due to their excellent thermal and flexible optical characteristics. Most of the existing studies have directly used different types and concentrations of nanofluids for SBS hybrid PV/T systems, focusing on the effect of adding nanofluids as frequency dividers on the system efficiency. However, there is still insufficient research on the effect of design parameters of nanofluids and experimental setups on the optical-thermal and PV conversion efficiency of the system, especially for water-based SiO2 nanoparticle fluids with significant potential applications.
Credit: HIGHER EDUCATION PRESS
As the globe grapples with the urgent need to shift from fossil fuels to sustainable energy sources, solar power stands as a beacon of hope. However, a significant challenge has been to efficiently capture and utilize the full spectrum of sunlight. Traditional photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight into electricity but can’t use the entire solar spectrum, especially the infrared part which is often wasted as heat. To address this, photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) systems have been developed. These hybrid systems not only generate electricity like PV panels but also capture the wasted heat, providing a dual benefit. The spectral beam splitting (SBS) technology can significantly enhance the collection temperature and system efficiency, and nanofluids commonly serve as splitters in the SBS hybrid PV/T system due to their excellent thermal and flexible optical characteristics. Most of the existing studies have directly used different types and concentrations of nanofluids for SBS hybrid PV/T systems, focusing on the effect of adding nanofluids as frequency dividers on the system efficiency. However, there is still insufficient research on the effect of design parameters of nanofluids and experimental setups on the optical-thermal and PV conversion efficiency of the system, especially for water-based SiO2 nanoparticle fluids with significant potential applications.
A research group of Xiaohui Yu from Hebei University of Technology uses water-based SiO2 nanofluid as a beam splitter for SBS hybrid PV/T systems, and investigates the effect of design parameters on system performance enhancement through actual transmissivity measurements and established PV and photothermal models.
It was found the transmissivity of the nanofluids to solar radiation gradually decreases with increasing SiO2 nanofluid concentration and optical path. The higher nanofluid concentration leads to a lower electrical conversion efficiency, a higher thermal conversion efficiency, and an overall system efficiency. The optimal SiO2 nanofluid concentration was 0.10 wt.%, striking a balance between efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Researchers also observed that increasing the optical path (from 0 to 30 mm) results in a 60.43% reduction in electrical conversion efficiency and a 50.84% increase in overall system efficiency. However, the overall system efficiency rises sharply as the optical path increases in the 0–10 mm range, and then slowly at the optical path of 10–30 mm. Additionally, the overall system efficiency increases first and then drops upon increasing the focusing ratio. The maximum efficiency is 51.93% at the focusing ratio of 3.
The findings of this study are of significant importance for selecting appropriate frequency division liquid and optimizing splitter design in SBS PV/T hybrid systems.
Journal
Frontiers in Energy
DOI
10.1007/s11708-024-0935-7
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Advancing performance assessment of a spectral beam splitting hybrid PV/T system with water-based SiO2 nanofluid
Article Publication Date
29-Mar-2024




