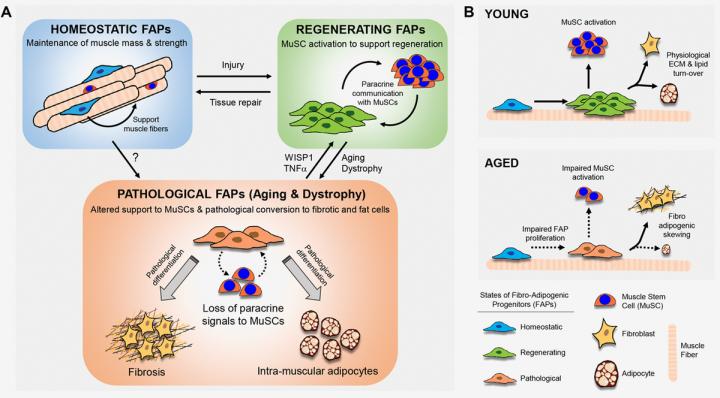
In adult skeletal muscle, loss of myofiber integrity caused by mechanical injuries or diseases are repaired by resident muscle stem cells, called satellite cells, which promptly exit from quiescence after disruption of muscle architecture to expand, diffe
Credit: Jerome N. Feige
[email protected]
In adult skeletal muscle, loss of myofiber integrity caused by mechanical injuries or diseases are repaired by resident muscle stem cells, called satellite cells, which promptly exit from quiescence after disruption of muscle architecture to expand, differentiate and drive tissue regeneration.
Dr. Jerome N. Feige from Nestlé Research, EPFL Innovation Park, Lausanne, Switzerland said, “Fibro/adipogenic progenitors constitute a population of interstitial mesenchymal cells in skeletal muscle which are devoid of myogenic potential, but support muscle stem cell commitment and can differentiate to the adipogenic or fibrotic lineages.”
Thus, FAPs are active regulators of cellular communication in skeletal muscle niche where they directly control tissue homeostasis and regeneration by supporting Mu SCs and myofibers.
In a recent study, the author’s lab investigated how aging influences the fate of FAPs and their cross-talk with Mu SCs to regulate the balance between myogenesis, adipogenesis and fibrosis in skeletal muscle.
Interestingly, aged FAPs fail to efficiently amplify following muscle injury and aging alters the capacity of FAPs to support Mu SC amplification and commitment.
Both in-vitro co-culture and in-vivo transplantation of young FAPs rejuvenate aged Mu SC function, but aged FAPs lose the ability to efficiently support Mu SCs.
The Feige Research team concluded, “FAPs are also likely a heterogeneous population and the clonal selection of different fates of FAPs during aging suggests a differential effect of age on distinct subpopulations.
While Tie2- expressing FAPs predominantly reside within neonatal and adult homeostatic muscles, another injury-activated subpopulation of FAPs characterized by Vcam1 expression is associated with regeneration of injured myofibers.”
###
Full Text – www.aging-us.com/article/102304/text
Correspondence to: Jerome N. Feige email: [email protected]
Keywords: muscle stem cell, regeneration, aging, fibro/adipogenic progenitor, niche
About Aging-US
Launched in 2009, Aging-US publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research as well as topics beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, cancer, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
To learn more about Aging-US, please visit www.Aging-US.com or connect with @AgingJrnl
Aging-US is published by Impact Journals, LLC to learn more please visit www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
Ryan James Jessup
[email protected]
202-638-9720
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




