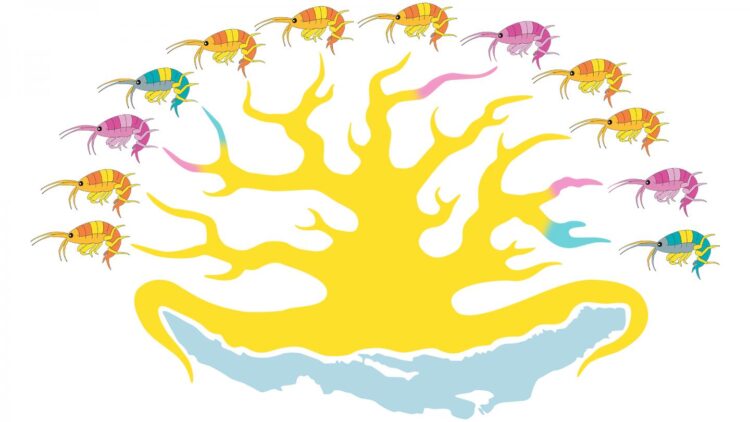
Credit: Valentina Burskaia/Skoltech
A group of scientists from Skoltech and the Institute for Information Transmission Problems of RAS (IITP RAS) showed, using Lake Baikal amphipods as an example, that parallel evolution driven by adaptations can be detected at the whole-genome level. The research was published in the Genome Biology and Evolution journal.
Similar adaptations are sometimes known to result from exactly the same mutations that occurred independently. The phenomenon is commonly termed “parallel evolution” to describe evolution that keeps repeating itself. It is usually hard to prove that such “parallel” mutations did not occur by pure accident but actually help organisms to adapt to their environment. Thus far, adaptive parallel mutations have been found in some individual genes or small groups of interrelated genes only.
A team of Skoltech and IITP RAS researchers led by Georgii Bazykin, an evolutionary biologist and a professor at Skoltech, undertook extensive bioinformatics analysis of protein-coding sequences of 46 amphipod species from Lake Baikal. The scientists were eager to see whether closely related amphipods from a Baikalian species flock displayed an elevated rate of adaptive parallel evolution.
The research suggests that adaptive parallel mutations are more common than random parallel mutations in protein-coding sequences of Lake Baikal amphipods and actually affect several thousand genes. Drawing on the basic laws of molecular evolution, the scientists showed that the mutations they discovered were indeed caused by the species’ need to adapt to the environment. However, the exact adaptations behind parallel evolution still remain a mystery.
“Lake Baikal is home to hundreds of species of endemic amphipods that evolved from several species in their distant ancestry and embrace a variety of ecological niches from predators to planktonic forms and parasites. Parallels were found even between forms with totally different lifestyles,” says Valentina Burskaia, the first author of the study and a Skoltech PhD student.
###
Skoltech is a private international university located in Russia. Established in 2011 in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Skoltech is cultivating a new generation of leaders in the fields of science, technology and business, is conducting research in breakthrough fields, and is promoting technological innovation with the goal of solving critical problems that face Russia and the world. Skoltech is focusing on six priority areas: data science and artificial intelligence, life sciences, advanced materials and modern design methods, energy efficiency, photonics and quantum technologies, and advanced research. Web: https:/
Media Contact
Ilyana Zolotareva
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.





