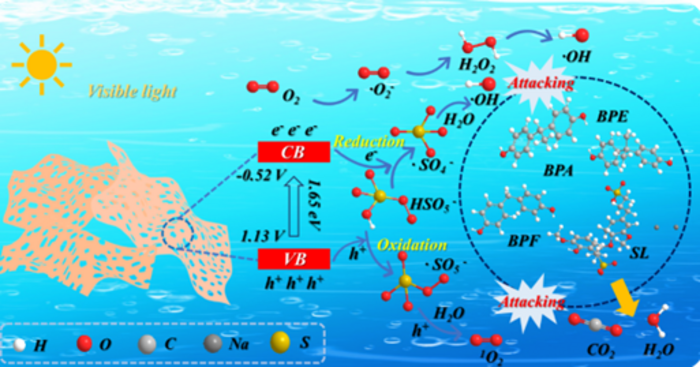
At present, the traditional ways to deal with the above two kinds of pollutants are mainly physical adsorption and biodegradation. The main disadvantages of these ways are incomplete treatment and long treatment period. Although the new photocatalytic technology uses clean energy and has mild reaction conditions, it also has the disadvantages of slow reaction speed and incomplete treatment. Compared with above ways to remove bisphenol pollutants and lignin derivatives, advanced technology to oxidize peroxymonosulfate has faster reaction rate and. However, it causes more metal ions to dissolve leading to secondary pollution to living organisms and the environment. To mitigate the issue, the ultimate solution should ideally combine photocatalytic technology and advanced peroxymonosulfate oxidation technology to eliminate the dissolution of metal ions—a team of researchers based in Canada did just that.
Credit: The Authors
At present, the traditional ways to deal with the above two kinds of pollutants are mainly physical adsorption and biodegradation. The main disadvantages of these ways are incomplete treatment and long treatment period. Although the new photocatalytic technology uses clean energy and has mild reaction conditions, it also has the disadvantages of slow reaction speed and incomplete treatment. Compared with above ways to remove bisphenol pollutants and lignin derivatives, advanced technology to oxidize peroxymonosulfate has faster reaction rate and. However, it causes more metal ions to dissolve leading to secondary pollution to living organisms and the environment. To mitigate the issue, the ultimate solution should ideally combine photocatalytic technology and advanced peroxymonosulfate oxidation technology to eliminate the dissolution of metal ions—a team of researchers based in Canada did just that.
researchers developed a new method for the synthesis of C-defects/C-O band-modified ultrathin porous carbon nitride, a material that has the potential to address this issue. “Carbon nitride has been widely used as a photocatalyst; however, conventional carbon nitrides have insufficient oxidizing ability and are not strong in activating peroxymonosulfate. This is largely due to their relatively small specific surface area and lack of active sites,” explained Jinguang Hu, corresponding author of the study.
Hu and his team constructed a porous ultra-thin carbon nitride material with C-defects and C-O bands using a one-step method. It can be synthesized by grinding and mixing urea nitrate, oxyacetic acid and urea evenly, and then directly thermally polymerizing in a muffle furnace. The catalyst not only increases specific surface area, but also the defect structure and doping elements to provide more active sites. Notably, the catalyst has very good photothermal performance which can accelerate the catalytic reaction process.
The team reported their study in the KeAi journal Green Energy and Environment.
“A large amount of bisphenol pollutants and lignin derivatives are constantly produced in the world,” noted Hu. “We believe this new advanced oxidation technology system can pave the way for the removal of such organic pollutants.”
###
Contact the corresponding author: Jinguang Hu, [email protected]
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Green Energy & Environment
DOI
10.1016/j.gee.2023.01.006
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Advanced oxidation via the synergy of C-defective/ C–O band modified ultrathin porous g-C3N4 and PMS for efficient photothermal degradation of bisphenol pollutants and lignin derivatives
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.




