Credit: Teemu Tomberg
Photoacoustic spectroscopy applied to background-free analyses was used to measure unprecedentedly small trace gas concentrations. Teemu Tomberg from the University of Helsinki developed detection methods that make it possible to measure extremely small traces of various gases.
Why should low concentrations be measured?
Trace gases denote substances that occur in very low quantities in air and other media. In spite of their low concentrations, trace gases can have a significant impact on the chemical properties of gaseous compounds. For this reason, their precise identification and quantification is important.
In his doctoral thesis, Teemu Tomberg focused on developing trace gas detection methods based on background-free laser absorption spectroscopy.
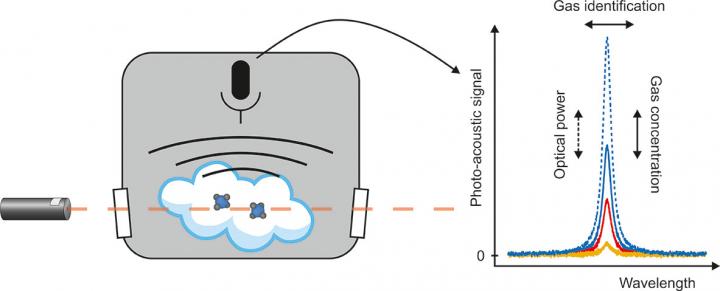
“Background-free means that an attempt is made to eliminate any interfering signals not originating from the target being measured,” Tomberg says.
The methods in question have special characteristics that make them well suited to detecting extremely low gas concentrations. Such characteristics include scalability with optical power combined with reduced sensitivity to optical power fluctuations.
Laser beams and soundwaves
In his thesis, Tomberg utilised two spectroscopic approaches: a novel interferometric method for the measurement of background-free broadband absorption spectra, and cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy.
The research was done at the Department of Chemistry of the University of Helsinki. Tomberg carried out his work in Laser Spectroscopy Group and his supervisors were Group leader, Associate professor Markku Vainio and Professor Lauri Halonen.
“I conducted the measurements in the mid-infrared region using a number of different laser light sources, such as optical parametric oscillators, optical frequency combs and quantum cascade lasers,” Tomberg says.
Among Tomberg’s achievements was demonstrating the new background-free interferometric measurement technique with the help of a state-of-the-art mid-infrared dual-comb spectrometer. The study was carried out at CREOL, the College of Optics and Photonics, under the supervision of Professor Konstantin Vodopyanov.
Through his measurements, Tomberg demonstrated that the new technique improves the signal-to-noise ratio of absorption spectroscopy by roughly a factor of five compared to regular direct absorption spectroscopy. The benefit gained was restricted by the low optical power of the lasers used, and the signal-to-noise ratio can in fact be further improved by using high-power lasers.
In investigating cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy, Tomberg reached record-level detection sensitivities by employing high optical power.
A competitor for coronavirus dogs?
The methods developed by Tomberg have interesting potential for applications.
Combining them with gas chromatography enables increasingly reliable analyses of even complex gas mixtures containing compounds with both small and large molecular weights. One such application would be an artificial nose for detecting diseases.
However, the advantage of dogs is their ability to detect coronavirus even without us knowing precisely which molecules they are smelling. For an artificial nose to function as intended, the relevant biomarker molecules to be measured should first be identified.
The study opens new avenues for developing equipment for field applications. Tomberg’s findings illustrate how laser absorption spectroscopy can be utilised as an advanced detector gas chromatograph, particularly in field applications where the compactness and maintenance-free operation of lasers are useful.
###
Reference:
Teemu Tomberg: Application of interferometry and cantilever-enhanced photo-acoustic spectroscopy to background-free trace gas detection. Doctoral dissertation (article-based), 2020. University of Helsinki, Faculty of Science, Department of Chemistry, Doctoral Programme in Chemistry and Molecular Research https:/
Teemu Tomberg is currently working at the University of Helsinki’s Faculty of Pharmacy where he is responsible for the construction of a new microscope utilising coherent Raman spectroscopy. The work is done in collaboration with the faculties of Science and Medicine.
More details:
Teemu Tomberg, [email protected], phone: +358 50 408 8246
Media Contact
Riitta-Leena Inki
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




