New workflow for annotating genomes will help both researchers and undergraduate students
Credit: Prashant Hosmani
As genome sequencing becomes cheaper and faster, resulting in an exponential increase in data, the need for efficiency in predicting gene function is growing, as is the need to train the next generation of scientists in bioinformatics. Researchers in the lab of Lukas Mueller, a faculty member of the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI), have developed a strategy to fulfill both of these needs, benefiting students and researchers in the process.
The Mueller Lab created a framework using the tremendous influx of new genome sequences as a training resource for undergraduates interested in learning genome annotation. This framework was published online in PLOS Computational Biology on April 3, 2019.
What is genome annotation, and why is it important?
After researchers determine the sequence of the millions of base pairs of DNA in an organism’s genome, they need to figure out two things: which DNA segments are genes that encode proteins, and what are those proteins’ functions. This process of identifying genes and predicting their functions is called genome annotation.
“The prediction of genes and their functions is what most biologists are interested in. That’s where most understanding of biological processes is happening,” says Prashant Hosmani, a Bioinformatics Analyst in the Mueller Lab and first author on the paper.
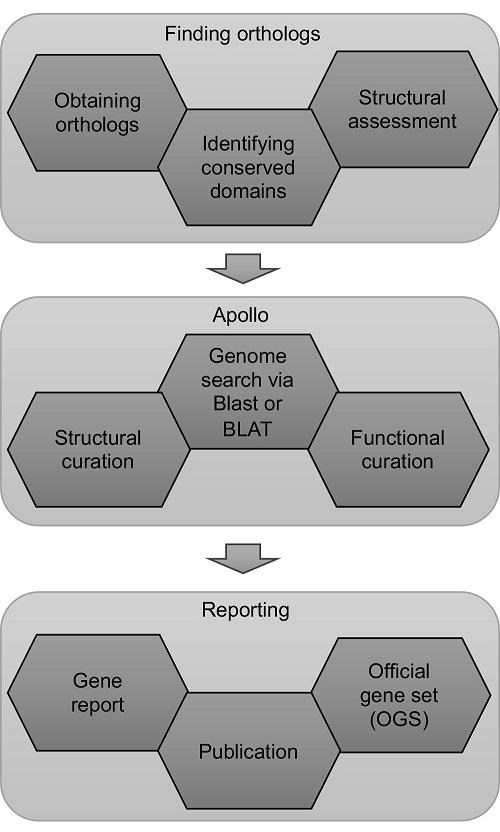
A genome is annotated by comparing its sequence to gene sequences from other related organisms. The most accurate method of genome annotation is manual curation, where a person does the analysis. In contrast, utilizing a computer program to identify genes and their functions is faster but is sometimes less accurate.
“Manual annotation is very time-intensive and thus expensive,” said Surya Saha, Senior Bioinformatics Analyst in the Mueller Lab and the project coordinator. “The trick is to do both: first use automatic annotation, and then focus on genes and biochemical pathways of interest and annotate them manually.”
The paper outlines a set of logical steps to begin an undergraduate annotation program from the ground up. When students first join the project, they are trained by team leaders and expert annotators on the tools of the trade.
Throughout the project, students keep careful notes of their research and results, ultimately compiling them into a report about the biochemical pathway of interest and the member gene families, which may be published. Indeed, this method has been used to generate a peer-reviewed publication with more than 20 undergraduate authors.
“Working is one thing, and receiving an acknowledgement for that work is also really important,” says Hosmani. “That acts as a real motivation for the students.”
Other student benefits include working with international collaborators, networking, practicing communication and peer review skills, and gaining valuable insights into career options. Undergraduates may also receive research or capstone project credits for their work, which increases their commitment to the project. More and more science-based graduate programs also require knowledge of bioinformatics, so these skills will prove valuable in many fields.
In the end, the researchers gain high-quality genome annotations for any species–not just plants–which offer a better understanding of how the organism functions, ultimately benefitting society in many fields, such as agriculture, biofuels and medicine.
The authors hope that other institutions will adapt and build upon this framework, no matter their size, access to resources or annotation goals. To make the framework easy to use, the authors designed their figures and tables to be stand-alone and printer-friendly for easy reference.
“Anybody who has a research problem, a sequenced genome, and interested students can implement a system by building off our workflow,” said Saha.
###
Media Contact
AJ Bouchie
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.



