Researchers at Osaka University find that a tadpole-like tunicate with nonconventional left-right patterning lacks the Nodal gene found in other chordates and uses Ca2+ oscillation and right-sided Bmp gene expression in embryonic development
Credit: Osaka University
Osaka, Japan – How does a developing embryo, which is initially round, tell left from right? This basic process is still poorly understood. However, investigating unusual cases can help shed light on how this process occurs in animals. More than a century ago, German biologist Dr. H. C. Delsman described unusual left-right (L-R) patterning in the tadpole-like tunicate Oikopleura dioica. Now, researchers at Osaka University have uncovered the details of this process in O. dioica, reported in a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
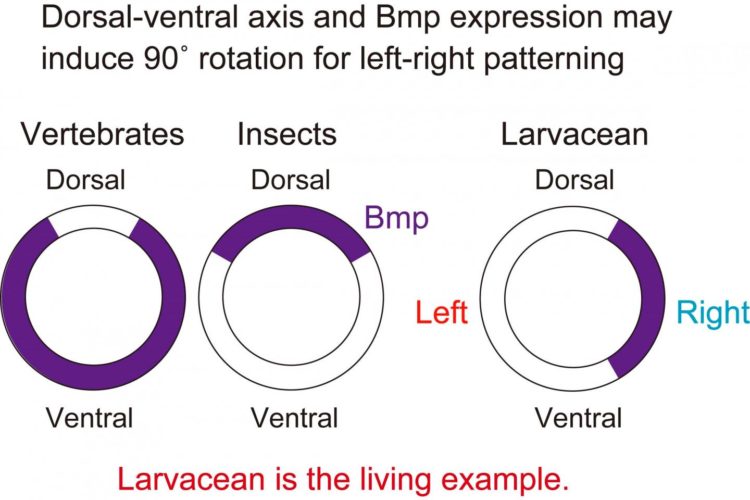
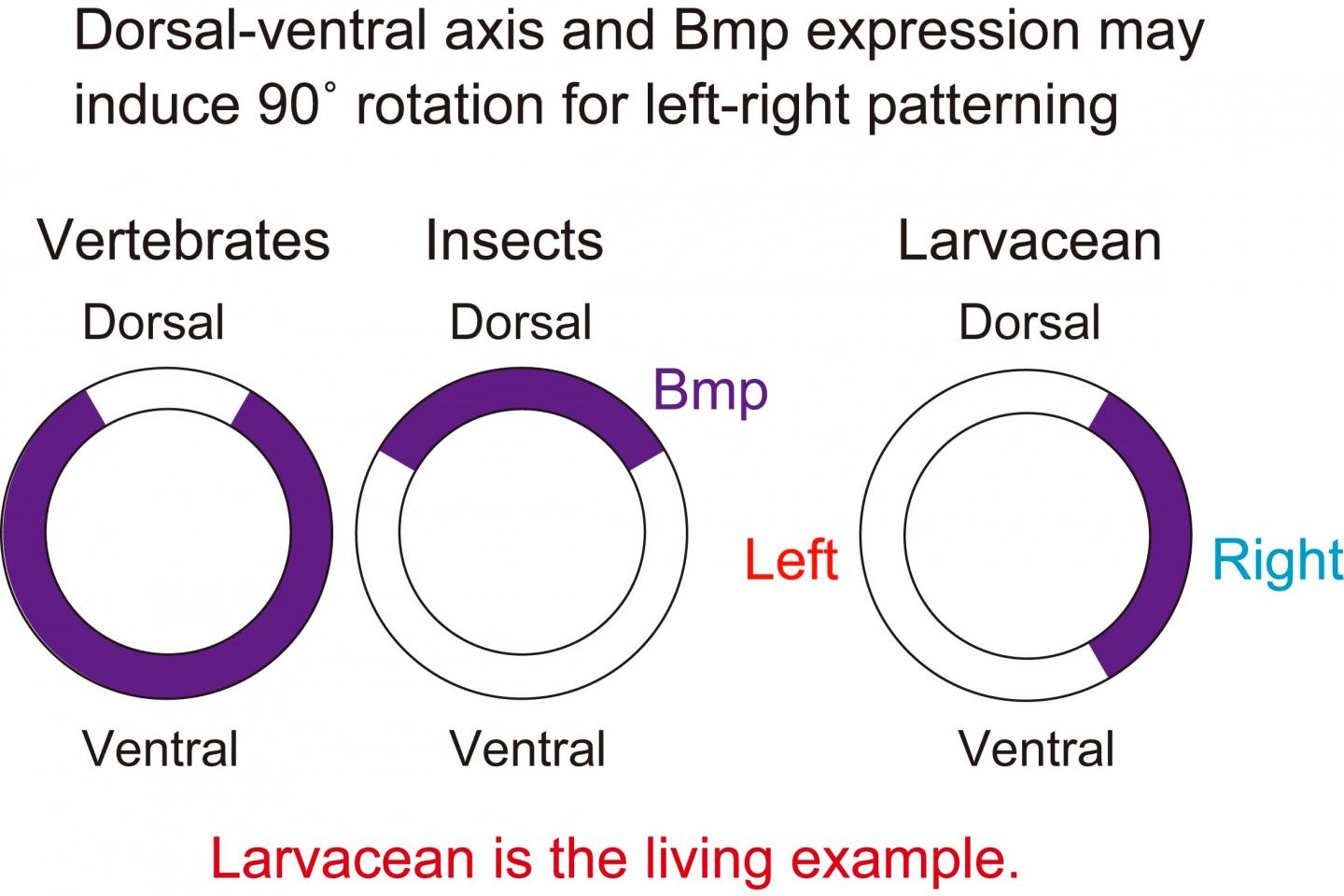
Bilateral symmetry is one the most fundamental characteristics of members of the phylum Chordata, the group that includes O. dioica as well as all animals with backbones, although L-R patterning tends to emerge later in development. However, in the larvacean tunicate O. dioica, distinct from other chordates, L-R asymmetry first appears in the four-cell embryo stage and persists throughout development; the nerve cord, typically located on the dorsal side of chordates, forms instead on the animal’s left side. This notable difference provides an opportunity to investigate the mechanisms that drive L-R patterning in chordates.
“Our study reveals that this larvacean uses calcium ion oscillation and expression of the right-sided bone morphogenetic protein (Bmp) gene for embryonic left-right patterning,” explains first author Takeshi A. Onuma. “Intriguingly, Nodal, an evolutionarily conserved left-determining gene found in other chordates, is absent from the genome of O. dioica. As the larvacean develops, it is likely that its tail twists 90° counterclockwise relative to its trunk, with the tail nerve cord localized on its left side.”
In most chordates, Nodal and Bmp create the gradient responsible for L-R determination in the developing embryo. The absence of Nodal, combined with the novel and early L-R patterning of this larvacean, is therefore of great interest for advancing understanding of the roles of Nodal, Bmp, and calcium ion oscillation, and the evolution of L-R patterning in early chordates.
According to senior author Hiroki Nishida, “between insects and vertebrates, the dorsal-ventral axis is inverted 180°, which is correlated with Bmp expression. However, the reason for this inversion is not yet well understood. In addition to revealing a novel left-right patterning process of a chordate species, our findings provide an example where the dorsal-ventral axis and Bmp expression lead to 90° rotation with left-right patterning.”
Such examples of novel L-R patterning are key for unraveling some of the most fundamental questions about the earliest evolution and development of chordates and other animals.
###
The article, “A chordate species lacking Nodal utilizes calcium oscillation and Bmp for left-right patterning,” was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences at DOI: https:/
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan’s most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university’s ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
Related Journal Article
http://dx.