Credit: IBB-UAB
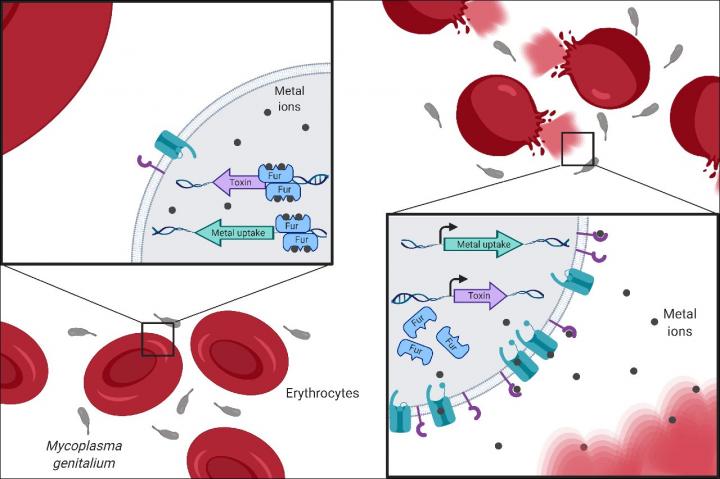
Metals (iron, zinc, nickel, cobalt, etc.) participate in numerous enzymatic reactions and are essential nutrients for bacteria. Inside our organism, these metals are scarcely available, because they are bound to proteins which preserve and transport them to the cells and tissues where they will be used.
During the infection process, bacteria compete with the organism in obtaining these metals. The response to metal starvation is often very virulent, bringing on strategies aimed to increase the supply of these elements. Metal acquisition is often achieved by releasing toxins, proteins that bind metals with high affinity and transporters that introduce these metals into the bacteria. In essence, these are highly sophisticated virulence mechanisms aimed at guaranteeing the support of essential nutrients needed for the bacteria’s survival.
A research team led by the Institute of Biotechnology and Biomedicine of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (IBB-UAB) has discovered the regulation and metal uptake systems of Mycoplasma genitalium (Mge). This emerging sexually transmitted pathogen is responsible for several genitourinary diseases and is becoming a superbacterium thanks to its emerging resistance to the antibiotics used against it. Researchers have managed to identify the protein that regulates metal uptake, the Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur), as well as other proteins responsible for transporting the metals into the microorganism.
“Through transcriptomic and proteomic techniques, we were able to determine the changes in Mge’s gene expression in the presence and absence of metals”, states Carlos Martínez, lead author of the study. “Moreover, we were able to identify the metals that bacteria require for growth using a mass spectrometry analysis developed by the UAB Analytical Chemistry Unit”, explains Sergi Torres, co-author of the study.
“The regulation and metal transport systems identified in Mge represent very attractive therapeutic targets. This study will allow us to develop strategies to block metal acquisition through inhibitors or immunotherapy”, says Òscar Quijada, researcher at the IBB-UAB and coordinator of the study.
In fact, researchers have already begun working in this direction, in collaboration with the UAB Department of Biophysics and the Microbiology Units of the Parc Taulí and Vall d’Hebron hospitals.
###
The research was recently published in the journal Emerging Microbes and Infections and included the involvement of researchers from the IBB, the UAB Department of Biophysics and the Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology.
Media Contact
María Jesús Delgado
[email protected]
34-935-814-049
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




