Credit: Jan Slapeta
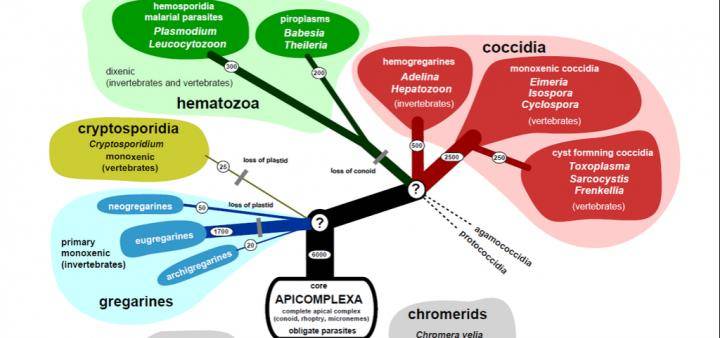
Apicomplexa form one of the largest and most diverse groups of obligate intracellular parasites, capable of infecting almost every kind of animal. It is estimated that between 1.2 and 10 million species exist, but only about 5,000-6,000 have been identified to date. These include Plasmodium (that causes malaria and about 440,000 deaths every year), Toxoplasma (that causes congenital disease and opportunistic infections in immunocompromised people), Babesia (that infects cattle), etc. Despite the global economic and health impact of these parasites, much of their biology is still unknown. For example, their surface is covered by glycoconjugates that are essential for their survival and infectivity, but little is known of the processes that lead to the synthesis of such molecules. In particular, one of the enzymes needed for the synthesis of important glycoconjugates had not yet been identified: the apicomplexan organisms do not have the GNA1 enzyme that fulfils this function in animals, plants and other eukaryotes.
In this study, the research team scanned the genome of P. falciparum and six other representative species of the phylum with the aim of identifying genes with GNA1-like activity. They identified and isolated a gene family with GNA1 function, which was confirmed by enzyme activity assays in vitro and by its capacity to restore growth in yeasts lacking GNA1. Furthermore, gene disruption by gene editing techniques such as CRISPR-CAS resulted in the absence of growth of parasites carrying the mutated gene, indicating that the protein is required for parasite viability. Sequence analyses indicate that the gene family has a single origin and evolved independently and parallel to its GNA1 counterpart (present in all other eukaryote organisms).
"Our results indicate that this enzyme is common to all members of the Apicomplexa phllyum and is likely essential for parasite growth. We are now analysing in detail its differences with human GNA1", explains lead author Marta Cova. "Because of its different origin, this enzyme could represent a good therapeutic target with selective action against all apicomplexans" adds Luis Izquierdo, ISGlobal researcher and coordinator of the study.
###
Media Contact
Adelaida Sarukhan
[email protected]
34-932-271-816
http://www.isglobal.org/en/
Original Source
https://www.isglobal.org/en/new/-/asset_publisher/JZ9fGljXnWpI/content/-identifican-una-posible-diana-terapeutica-contra-un-extenso-grupo-de-parasitos http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22441-3