Credit: Adapted from ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c00942
According to the American Heart Association, heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide in recent years. During a heart attack, or myocardial infarction (MI), a blocked artery and the resulting oxygen deprivation cause massive cardiac cell death, blood vessel impairment and inflammation. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering have developed a cardiac patch with tiny engineered blood vessels that improved recovery from MI in rats and pigs.
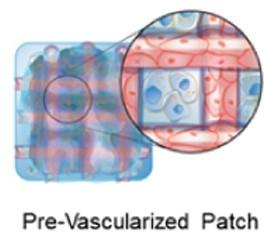
To effectively treat MI, lost heart muscle tissue must regenerate and new blood vessels must form to restore oxygen and nutrients to cells. Scientists have tried to develop patches containing various therapeutic cells to treat MI, but so far most have been too cumbersome to make, or they don’t restore both cardiac muscle and blood supply to the injured site. Ke Cheng and colleagues previously developed a relatively easy-to-make pre-vascularized cardiac patch, which contained engineered microvessels in a fibrin gel spiked with cardiac stromal cells. When implanted into rats after an MI, the cells in the patch secreted growth factors that made cardiac muscle and blood vessels regrow. Now, the researchers wanted to test the patch further in rats, as well as in pigs, which have cardiovascular systems more similar to humans than those of rodents.
The researchers implanted the cardiac patch in rats that recently had a heart attack. Four weeks later, rats that received the patch had less scar tissue, increased cardiac muscle and improved cardiac pump function compared with untreated rats. The team observed similar effects in pigs that had undergone MI and were treated with the patches. The patch increased recruitment of the pigs’ progenitor cells to the damaged area and enhanced the growth of new blood vessels, as well as decreased cardiac cell death and suppressed inflammation. Although prior studies have used blood vessel-forming cells or natural blood vessels to vascularize cardiac patches, this study is the first to demonstrate the success of pre-vascularized cardiac stromal cell patches using microengineered synthetic blood vessels for treating MI in a large animal model. More studies on the mechanisms, safety and efficacy of patch repair are needed before the technology can be applied to humans, the researchers say.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, the National Science Foundation, the North Carolina State University Chancellor’s Innovation Fund and the UNC General Assembly Research Opportunities Initiative.
The abstract that accompanies this paper is available here.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and its people. The Society is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]




