Credit: Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO)
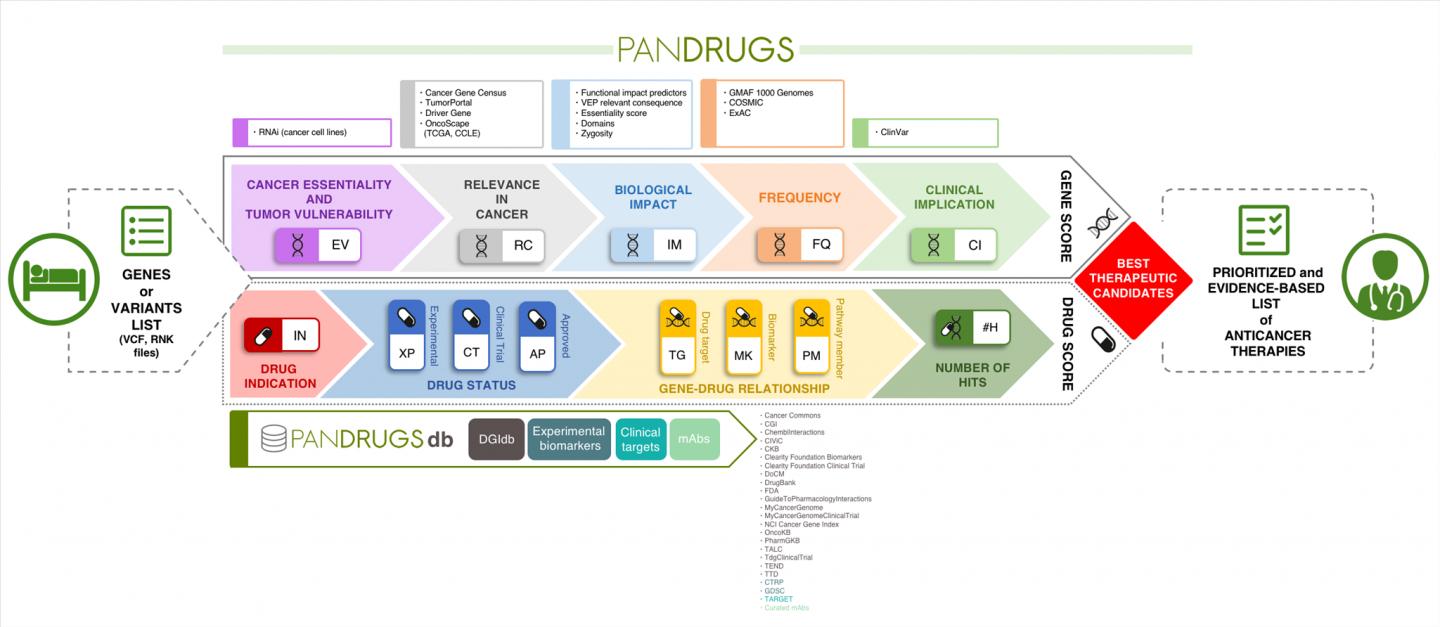
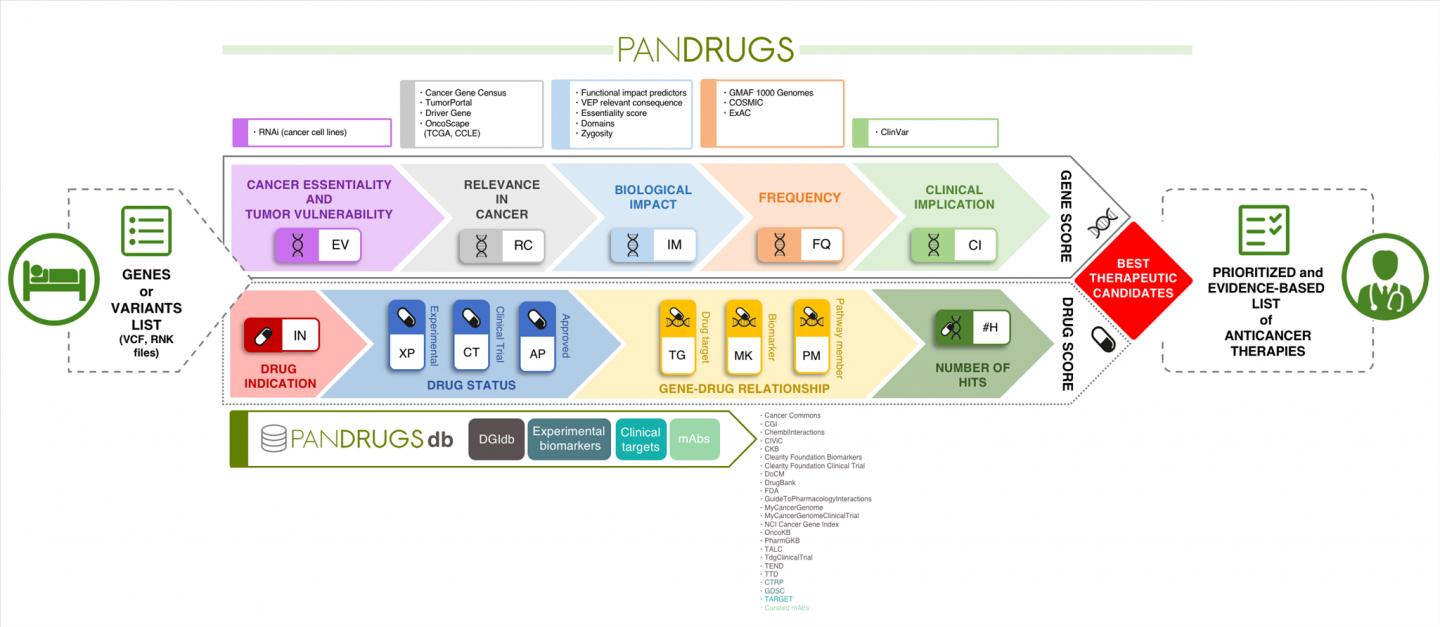
Identify and prioritize treatment options based on a patient's profile of genetic alterations is a major challenge in personalized cancer medicine. Data-driven approaches such as PanDrugs can help to this end. This new computational resource has been developed by researchers from the Bioinformatics Unit at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) and is described in a paper published in Genome Medicine.
A large majority of cancers carry a long list of genetic alterations whose biological and clinical relevance, and susceptibility to be pharmacologically-targeted isn't always clear. Several tools have been developed to identify clinically actionable genomic alterations and to suggest targeted therapies but they have some limitations and there's still a gap between raw genomic data and clinical usefulness.
To overcome this, researchers lead by Fátima Al-Shahrour, head of the Bioinformatics Unit at the CNIO, have implement this novel method called PanDrugs. "The main novelty introduced in this methodology compared with current tools is the broadening of the search space to provide therapeutic options", explains Al-Shahrour.
In other words, PanDrugs suggests treatments for direct targets (e.g. genes that contribute to disease phenotype and can be directly targeted by a drug) and biomarkers (e.g. genes that have a genetic status associated with drug response but the protein product is not the drug target itself). But also, PanDrugs integrates a systems biology knowledge-based layer that automatically inspects biological circuits expanding cancer candidate therapies from beyond limited cancer-related gene lists to the whole druggable pathway.
"This novel strategy (called 'pathway member') extends the treatment opportunities of cancer patients by enriching the therapeutic arsenal against tumours and opens new avenues for personalized medicine", states Al-Shahrour. Thanks to pathway member strategy, the paper describes how PanDrugs is able to identify treatments used in clinical practice that might benefit prostate, breast and colorectal cancer patients without druggable cancer driver altered genes.
Researchers emphasize that PanDrugs database represents, by itself, a remarkable contribution. "This database is the largest public repository of drug-target associations available from well-known targeted therapies to preclinical drugs. Current version of PanDrugsdb integrates data from 24 primary sources and supports >56000 drug-target associations".
PanDrugs can be fully integrated with custom pipelines through its programmatic API and its docker image facilitates PanDrugs in-house installation, enhancing reproducibility and improving performance. PanDrugs and PanDrugsdb are open-source and fully available at http://www.pandrugs.org.
###
Media Contact
Cristina de Martos
[email protected]
34-917-328-000
@CNIO_Cancer
Original Source
https://www.cnio.es/ing/publicaciones/a-novel-data-driven-method-to-personalise-cancer-treatment http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13073-018-0546-1