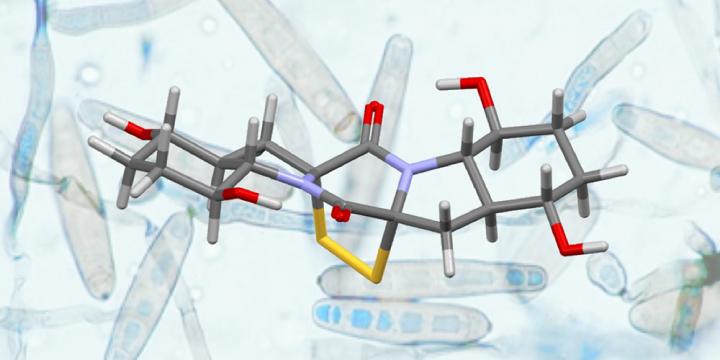
Credit: University of Basel, Olivier Baudoin with permission from G. Roberts
Chemists from the University of Basel have succeeded in synthesizing two complex natural products from the group of dithiodiketopiperazines (DTPs). For this, they employed a new strategy based on “C-H bond activation,” resulting in a short and high yielding route. In the most recent edition of the Journal of the American Chemical Society, the researchers describe their new concept for the total synthesis of Epicoccin G and Rostratin A.
Certain microorganisms, such as fungi, are a rich source of secondary metabolites, which have great potential in medicinal applications. Of particular interest among these secondary metabolites are the dithiodiketopiperazines (DTPs), as they possess a variety of interesting biological activities that could be used in the development of new drugs for malaria or cancer. However, despite extensive efforts over the past decade, relatively few total syntheses of these molecules have been completed and obtaining the necessary quantities for further investigation remains a challenging target.
Professor Olivier Baudoin and first author Pierre Thesmar from the Department of Chemistry at the University of Basel have now succeeded in the development of an efficient and scalable synthesis of two of these structurally challenging natural products.
C-H bond activation as a new synthetic strategy
The synthesis route used by the Basel team employed a new strategy for the ring system construction involving a method known as “C-H bond activation,” which in recent years has become a valuable synthetic tool. In this key step, two rings are simultaneously formed by a twofold reaction in which a carbon-hydrogen bond (C-H bond) is cleaved and a carbon-carbon bond (C-C bond) formed. This route allows efficient access to a common intermediate on multigram quantities from inexpensive, commercially available starting materials.
This intermediate was then converted to the first natural DTP, Epicoccin G, in seven additional steps. Compared with the previous single total synthesis of the same molecule, the current synthesis displays 14 steps instead of 17, and a much higher overall yield of 19.6% rather than 1.5%.
Next challenge: Rostratin A
Following the successful synthesis of Epicoccin G, the research team ventured to synthesize Rostratin A, a related natural DTP, for the first time and on a larger scale. This molecule displays a number of daunting structural elements that necessitated a significant adaptation of the synthesis end-game. After much experimentation, optimization of each step and validation on multigram quantities, Rostratin A was synthesized on a 500 mg scale. Overall, this total synthesis was completed in 17 steps and with a high overall yield of 12.7%.
The new strategy reveals the high potential of the C-H bond activation method in the field of natural product synthesis. In a next step, the researchers aim to synthesize other natural DTPs and their analogues in order to conduct more advanced studies and further evaluate the medicinal potential.
###
Further information
Prof. Dr. Olivier Baudoin, University of Basel, Department of Chemistry, phone +41 61 207 1198, email: [email protected]
Media Contact
Iris Mickein
[email protected]
41-612-072-425
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




