Using lasers to slow down atoms is a technique that has been used for a long time already: If one wants to achieve low-temperature world records in the range of absolute temperature zero, one resorts to laser cooling, in which energy is extracted from the atoms with a suitable laser beam.
Credit: TU Wien
Using lasers to slow down atoms is a technique that has been used for a long time already: If one wants to achieve low-temperature world records in the range of absolute temperature zero, one resorts to laser cooling, in which energy is extracted from the atoms with a suitable laser beam.
Recently, such techniques have also been applied to small particles in the nano- and micro-metre range. This already works quite well for individual particles – but if you want to cool several particles at once, the problem turns out to be much more difficult. Prof. Stefan Rotter and his team at the Institute of Theoretical Physics at TU Wien have now presented a method with which extremely effective cooling can also be achieved in this case.
Not just a beam, but a whole light pattern
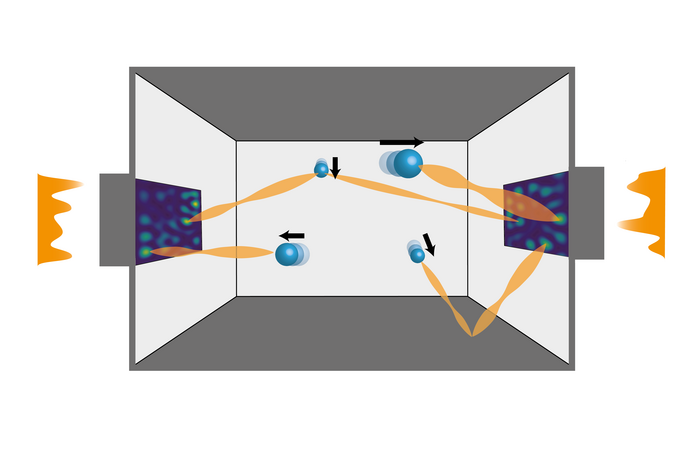
“In laser cooling of atoms, one uses only an ordinary laser beam. However, this approach does not work for cooling nano-particles. Our trick now is to continuously adapt the spatial structure of the laser beam to the particle motion in such a way that optimal cooling is implemented at every point in time,” says Stefan Rotter. “With the method we have developed, you can very quickly calculate how this light pattern must look like. While the particles change their positions, you continuously adjust the light pattern and can thus continuously decelerate the particles,” adds Jakob Hüpfl, who is researching this topic as part of his doctoral thesis.
Interestingly, to use the new method, you don’t need to know where the particles are located – you don’t even need to know how many particles there are and how they move. You simply send light through the system and measure how this light is changed by the particles. From this, the optimal light pattern is determined with which the particles must be irradiated at the next moment in order to slow them down a bit more – until their movement finally “freezes”. So far, this is only theoretical work, but experiments are already underway.
Journal
Physical Review Letters
DOI
10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.083203
Article Title
Optimal Cooling of Multiple Levitated Particles through Far-Field Wavefront Shaping
Article Publication Date
22-Feb-2023




