Oncologists at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center have successfully treated a patient with metastatic melanoma by combining two different types of immunotherapy. Cassian Yee and colleagues describe their approach in a paper, "Combined IL-21-primed polyclonal CTL plus CTLA4 blockade controls refractory metastatic melanoma in a patient," that will be published online May 30 in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Melanoma is the most serious form of skin cancer, accounting for the vast majority of skin cancer deaths when it spreads, or metastasizes, to other organs in the body. Many approaches to treating metastatic melanoma are based on boosting the immune system's ability to target and destroy the tumor. One strategy is to isolate pure populations of the patient's T cells that can target the melanoma and then transfer them back into the patient. Another approach is to treat patients with ipilimumab, an antibody that activates the patient's existing antitumor T cells by blocking the function of a protein called CTLA4. On their own, both treatments can slow the progression of metastatic melanoma, but they are rarely able to send the disease into complete remission. Yee and colleagues wondered whether combining the two approaches might be more effective.
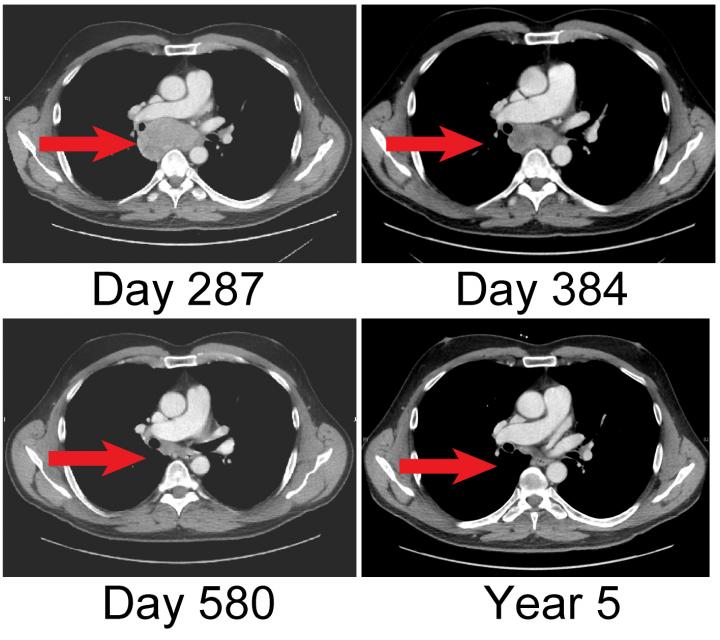
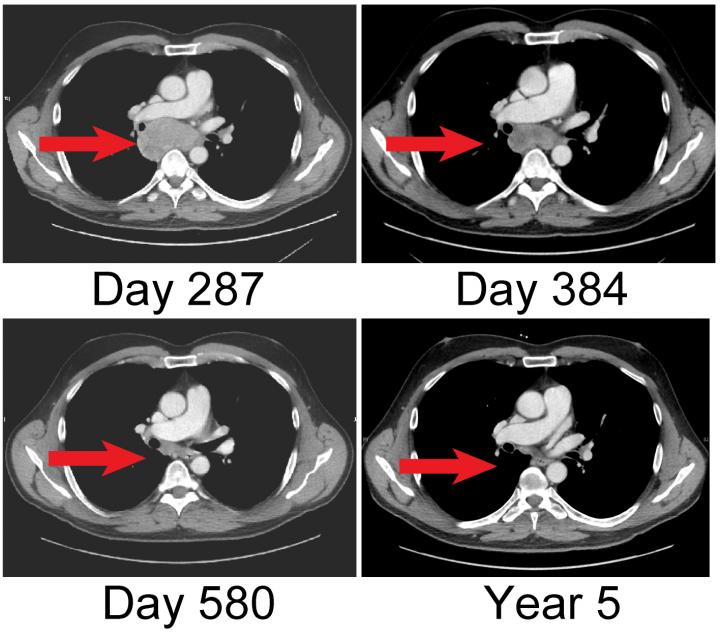
The researchers tested their idea on a 53-year-old patient with multiple metastases who had previously shown little response to either T cell transfers or ipilimumab treatment. The patient now received an infusion of his own antitumor T cells that had been treated with an immune signaling protein, called interleukin-21, that promotes T cell survival. Immediately afterward, the patient received a dose of ipilimumab. Within weeks, the patient's tumors began to shrink, and they eventually disappeared completely. Yee and colleagues report that, over five years later, the patient remains disease free.
The researchers found that their combined approach boosted the number of antitumor T cells circulating in the patient's blood in both the short and long term. Moreover, the enhanced immune response induced by this treatment allowed the patient to develop new types of T cells that attacked the melanoma in additional ways, a phenomenon known as epitope spreading.
"Combining CTLA4 blockade with the transfer of well-characterized, robust antitumor T cells represents an encouraging strategy to enhance the activity of the adoptively transferred T cells and induce antitumor responses," says Yee, who now works at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. "This strategy may hold broad promise for ipilimumab-resistant melanomas."
###
Chapuis et al. 2016. J. Exp. Med. http://dx.doi.org/10.1084/jem.20152021
About The Journal of Experimental Medicine The Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM) is published by The Rockefeller University Press. All editorial decisions on submitted manuscripts are made by research-active scientists in conjunction with our in-house scientific editors. JEM provides free online access to many article types immediately, with complete archival content freely available online since the journal's inception. Authors retain copyright of their published works, and third parties may reuse the content for non-commercial purposes under a Creative Commons license. For more information, please visit jem.org. Follow us on Twitter at @JExpMed and @RockUPress.
Media Contact
Ben Short
[email protected]
212-327-7053
@RockUPress
http://www.rupress.org/
The post A combined approach to treating metastatic melanoma appeared first on Scienmag.