Device that works in rats has potential to replace electronic stimulators, drugs for pain, incontinence
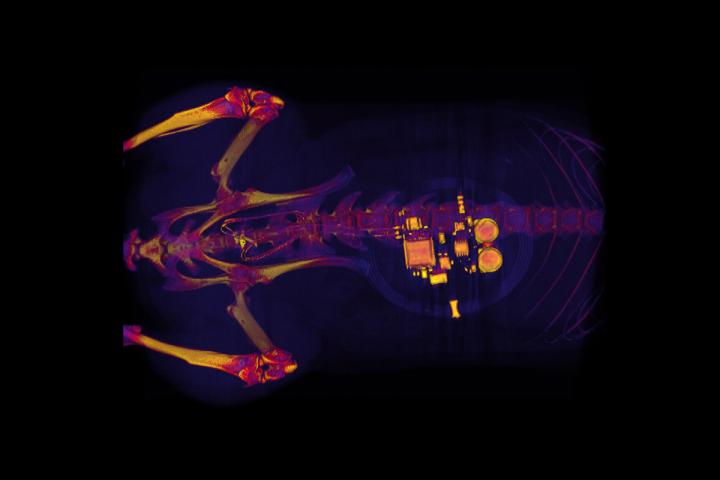
Credit: GEREAU LAB, Washington University
A team of neuroscientists and engineers has developed a tiny, implantable device that has potential to help people with bladder problems bypass the need for medication or electronic stimulators.
The team — from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and the Feinberg School of Medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago — created a soft, implantable device that can detect overactivity in the bladder and then use light from tiny, biointegrated LEDs to tamp down the urge to urinate.
The device works in laboratory rats and one day may help people who suffer incontinence or frequently feel the need to urinate.
The new strategy is outlined in an article published Jan. 2 in the journal Nature.
Overactive bladder, pain, burning and a frequent need to urinate are common and distressing problems. For about 30 years, many with severe bladder problems have been treated with stimulators that send an electric current to the nerve that controls the bladder. Such implants improve incontinence and overactive bladder, but they also can disrupt normal nerve signaling to other organs.
“There definitely is benefit to that sort of nerve stimulation,” said Robert W. Gereau IV, PhD, the Dr. Seymour and Rose T. Brown Professor of Anesthesiology at Washington University School of Medicine, and one of the study’s senior investigators. “But there also are some off-target side effects that result from a lack of specificity with those older devices.”
Gereau and his colleagues developed the new device in hopes of preventing such side effects.
During a minor surgical procedure, they implant a soft, stretchy belt-like device around the bladder. As the bladder fills and empties, the belt expands and contracts. The researchers also inject proteins called opsins into the animals’ bladders. The opsins are carried by a virus that binds to nerve cells in the bladder, making those cells sensitive to light signals. This allows the researchers to use optogenetics — the use of light to control cell behavior in living tissue — to activate those cells.
Using blue-tooth communication to signal an external hand-held device, the scientists can read information in real time and, using a simple algorithm, detect when the bladder is full, when the animal has emptied its bladder, and when bladder emptying is occurring too frequently.
“When the bladder is emptying too often, the external device sends a signal that activates micro-LEDs on the bladder band device, and the lights then shine on sensory neurons in the bladder. This reduces the activity of the sensory neurons and restores normal bladder function,” Gereau said.
The researchers believe a similar strategy could work in people. Devices for people likely would be larger than the ones used in rats, and could be implanted without surgery, using catheters to place them through the urethra into the bladder.
“We’re excited about these results,” said John A. Rogers, PhD, the study’s other senior investigator and a professor of materials science and engineering at Northwestern. “This example brings together the key elements of an autonomous, implantable system that can operate in synchrony with the body to improve health: a precision biophysical sensor of organ activity; a noninvasive means to modulate that activity; a soft, battery-free module for wireless communication and control; and data analytics algorithms for closed-loop operation.”
Closed-loop operation essentially means the device delivers the therapy only when it detects a problem. When the behavior is normalized, the micro-LEDs are turned off, and therapy can be discontinued.
Gereau and Rogers expect to test similar devices in larger animals. The researchers also believe the strategy could be used in other parts of the body — treating chronic pain, for example, or using light to stimulate cells in the pancreas to secrete insulin. One hurdle, however, involves the viruses used to get light-sensitive proteins to bind to cells in organs.
“We don’t yet know whether we can achieve stable expression of the opsins using the viral approach and, more importantly, whether this will be safe over the long term,” Gereau said. “That issue needs to be tested in preclinical models and early clinical trials to make sure the strategy is completely safe.”
###
Mickle AD, et al. A wireless closed-loop system for optogenetic peripheral neuromodulation. Nature, Jan. 2, 2019.
This work was supported by an NIH Director’s Transformative Research Award, an NIH SPARC Award from the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences and the National Institute on Drug Abuse, of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), grant numbers TR01 NS081707, U18 ED021793, R01 NS42595, F32 DK115122, T32 DA007261, T32 DK108742, T32 GM108539, DK082315 and K08 DK094964, and the Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer’s Network, DIAN UF1AG032438. Additional funding from the McDonnell Center for Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, the Urology Care Foundation Research Scholars Program and the Kailash Kedia Research Scholar Endowment, the National Science Foundation, the Ryan Fellowship and the Northwestern University Institute for Nanotechnology.
Washington University School of Medicine’s 1,500 faculty physicians also are the medical staff of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children’s hospitals. The School of Medicine is a leader in medical research, teaching and patient care, ranking among the top 10 medical schools in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. Through its affiliations with Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children’s hospitals, the School of Medicine is linked to BJC HealthCare.
Media Contact
Jim Dryden
[email protected]
314-286-0110




