Credit: Kanazawa University
Boundaries between different regions of the brain are essential for the brain to function. Research to-date has shown that molecular machineries located at the cell membrane such as cell adhesion molecules are responsible for regulating the boundary formation. Specifically, Slit and Netrin are diffusible guidance molecules that regulate the attraction and/or repulsion of the cells. Cells that receive Slit or Netrin are repelled from its source. However, it is also known that some cells are attracted to the source of Netrin. Makoto Sato at Kanazawa University and colleagues report in iScience that these diffusible molecules are essential for the boundary formation in fly brains.
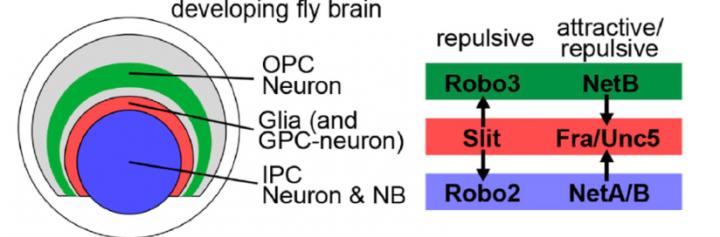
The visual center of the adult fly brain can stem from two parts of the larval fly brain, the inner proliferation center (IPC) and the outer proliferation center (OPC). Glial cells separate the IPC neurons and OPC neurons (Fig. 1). Keeping the IPC and OPC separated ensures that they give rise to distinct brain regions.
Netrin becomes effective when received by the two receptor molecules Fra and Unc5. To examine the effects of Netrin, the researchers used gene editing and inactivated it in the larva visual centers. These flies were found to have the IPC neurons penetrating the OPC, with disrupted distribution of the OPC neurons and glial cells (Fig. 3). The same effects were seen in Fra and Unc5 inactivated flies. Similarly, Slit becomes active when bound to its receptor, Robo. Inactivation of either Slit or Robo resulted in similar boundary defects.
The researchers also found that Netrin expressed in the IPC and OPC neurons is received by Fra and Unc5 expressed in the glial cells situated between the IPC and OPC. In contrast, Slit expressed in the glial cells is received by Robo expressed in the IPC and OPC (Fig. 1).
These unique findings are important because the guidance molecules are different from molecules that act at cells membranes. However, it is very difficult to imagine how these guidance molecules govern the boundary formation. So, Sato and his team formulated a mathematical model of the functions of Slit and Netrin, and demonstrated that these guidance molecules can indeed regulate the formation of boundaries.
The exchange of Slit and Netrin with their respective partners, between the neurons and glial cells were simulated. Slit produced by glial cell always repels neurons. However, given that Netrin possesses attractive and repulsive properties, then how does Netrin function? The key idea of their model is that Netrin produced by neurons attracts glial cells when its concentration is low. But it is switched to become repellent when its concentration is high. This model shows that the balance between attraction and repulsion between neurons and glial cells regulates the boundary formation in the different brain regions (Fig. 2). Thus, the report establishes a link between the diffusible guidance molecules and the boundary formation mechanism in multicellular organisms.
“Since these signaling pathways are evolutionarily conserved from insects to mammals, their roles in establishing the tissue border may also be conserved across species”, the team concludes. An elucidation of these novel pathways paves the way for preventing structural and thereby functional deformities in the brains of higher species, such as humans. Inhibition of cell mixing also aids in keeping toxic cells, such as cancer cells, from invading healthy ones.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
81-762-645-076
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




