Credit: ITMO University
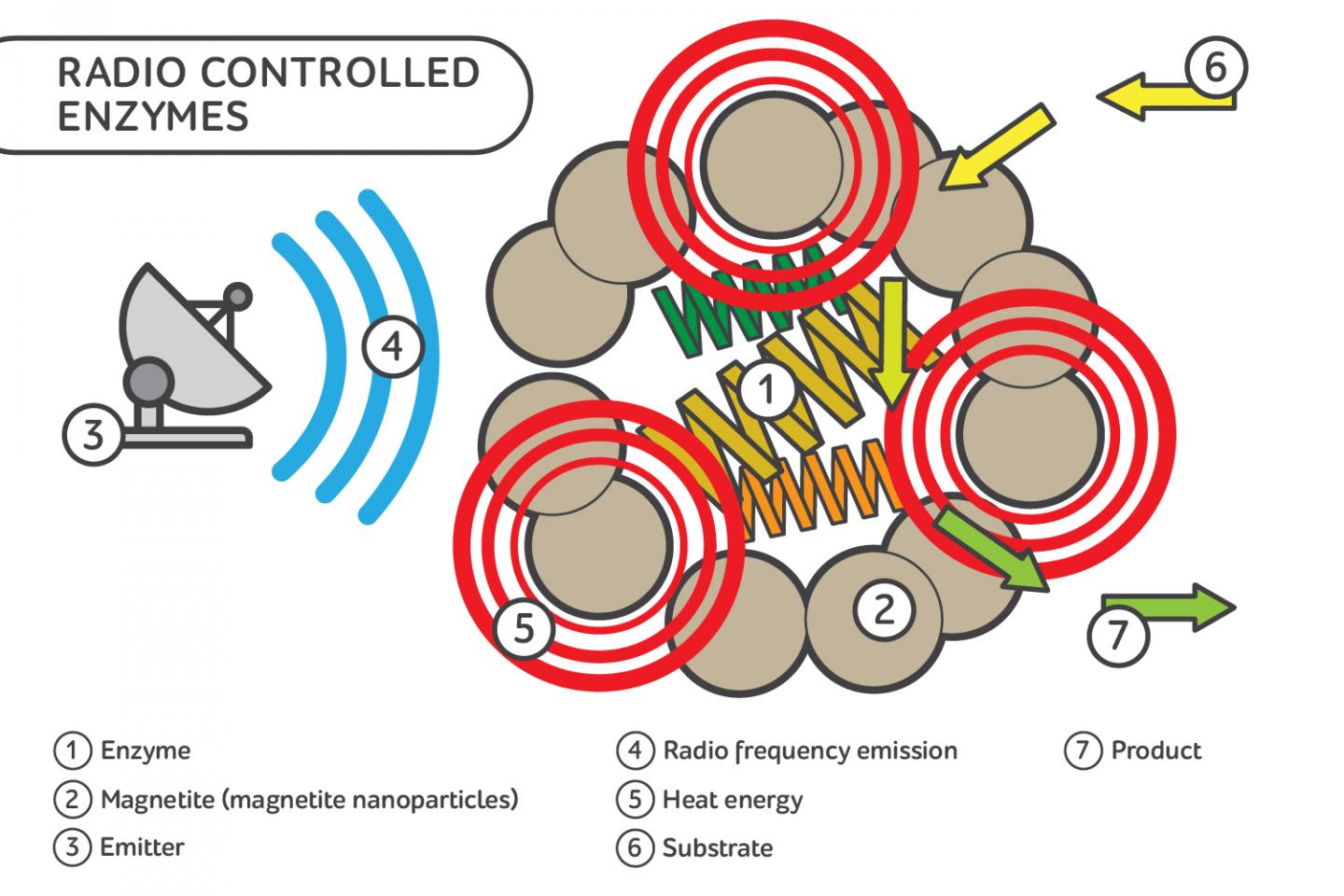
Scientists developed a method to enhance the activity of enzymes by using radio frequency radiation. The method requires making a special complex consisting of enzymes and magnetic nanoparticles. The particles can adsorb radio emission and convert it to heat, resulting in enzymatic processes acceleration by more than four times. Such method can be used to create radio-controlled biochemical systems and adjust metabolism in living organisms. The results are published in ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.
Enzymes are involved in a variety of reactions in living organisms, and their effectiveness depends on a variety of conditions. Although usually the enzyme activity is controlled chemically, researchers from ITMO University showed that this can be done remotely using physical methods such as radio frequency field.
To make radio-controlled enzymes, the scientists synthesized a special complex in which an enzyme is enclosed in a rigid porous framework of magnetite nanoparticles. Whenever the radio field is applied, the nanoparticles adsorb radio emission and heat up, passing additional energy to the enzyme and resulting in the enzymatic reaction rate acceleration. An experiment conducted on a model enzyme, carbonic anhydrase, demonstrated that the reaction rate can be increased by more than four times.
"There are very few studies out there that explore enzyme manipulation through the radio waves. We were the first who managed to increase the activity of a non-thermostable enzyme. Typically, these enzymes change the conformation at high temperatures and then stop working. But placed within the rigid framework of nanoparticles, the enzyme is stabilized from structure rearrangements as the nanoparticles mechanically restrict the enzyme mobility," comments Andrey Drozdov, member of ITMO University's SCAMT Laboratory.
There are two key parameters among the advantages of the radio emission used in the work. On the one hand, such radio waves can easily go through the tissues, and on the other, they are absolutely harmless to the body. Thus, by using the radiofrequency field, you can control the activity of enzymes in the body and adjust cell metabolism. In the near future, scientists plan to try out this method on other enzymes in an attempt to influence the vital activity of bacteria or cells.
Since this topic has a lot of potentials, further work will focus on using the technique with other enzymes, as well as in living cells. For example, it is still unclear whether it is possible with this method to make bacteria or cells divide more often or, on the contrary, to stop their division," notes Yulia Andreeva, the first author of the study.
###
Reference: Enzymatic Nanocomposites with Radio Frequency Field-Modulated Activity. Yulia I. Andreeva et al. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering. 30 October, 2018
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00838
Media Contact
Dmitry Malkov
[email protected]
7-953-377-5508
@spbifmo_en
http://en.ifmo.ru/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00838