Credit: Caspar M. Schwiedrzik
Every five seconds we close our eyes and blink to moisten them. During this brief moment no light falls on our retina yet it is not constantly dark and we continue to observe a stable picture of our environment. The brain seems to remember the percepts that have just happened. Caspar Schwiedrzik and Sandrin Sudmann, neuroscientists at the German Primate Center and the University Medical Center Göttingen, have in cooperation with colleagues from the United States performed studies on epilepsy patients to determine where this memory is situated in the brain and how it works. They have identified a brain area that plays a crucial role in perceptual memory. This finding enables a better understanding of the interaction of perception and memory (Current Biology).
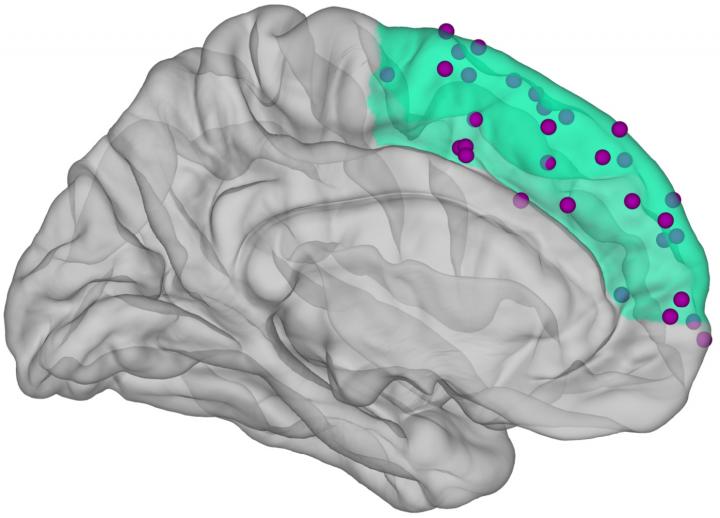
Even though we constantly blink and move our head and eyes, we still see our world as a stable, unified whole. It must therefore be possible for the brain to retain visual information for a short period of time and then put it together to form a conclusive image without interruptions. Caspar Schwiedrzik and his team of neuroscientists suspected that a specific brain region known as the medial prefrontal cortex which plays an important role in short-term memory and decision-making may be a key player in this process.
At New York University the scientists had the opportunity to study this region of the brain in patients with epilepsy. To treat their disease, electrodes were temporarily implanted in the brain of these patients. Subjects were shown a dot lattice on a screen and were asked to indicate their perception of the orientation (for example horizontal or vertical) of the points. They were then shown a second dot lattice and were asked to indicate the orientation of the points. If both orientations were the same, this was interpreted as an indication that the subjects used the information from the first round to establish a conclusive percept in the second round. While the subjects performed the task, their neural activity in the prefrontal cortex was recorded. In one of the subjects a section of the superior frontal gyrus was removed due to an earlier illness and she was unable to store the visual information.
"Our research shows that the medial prefrontal cortex calibrates current visual information with previously obtained information and thus enables us to perceive the world with more stability, even when we briefly close our eyes to blink," says Caspar Schwiedrzik, first author of the study and scientists at the German Primate Center and at the University Medical Center Göttingen. This is not only true for blinking but also for higher cognitive functions. "Even when we see a facial expression, this information influences the perception of the expression on the next face that we look at," says Schwiedrzik.
"We were able to show that the prefrontal cortex plays an important role in perception and in context-dependent behavior," says Schwiedrzik, summarizing the findings of the study. In further studies, the researchers want to investigate, among other things, the role that confidence in one's own perception plays in perceptual memory.
###
Media Contact
Dr. Caspar M. Schwiedrzik
[email protected]
49-055-139-12358
http://dpz.eu