Credit: Courtesy of Dr. Toshinori Fujie, Waseda University
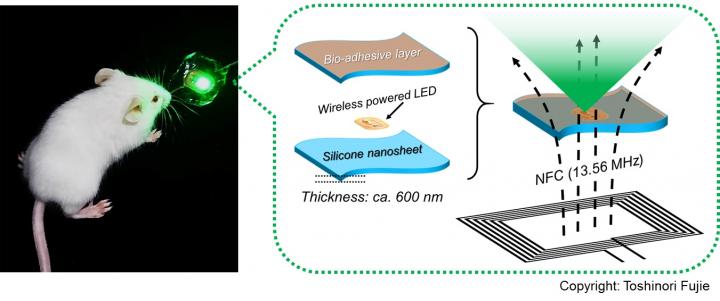
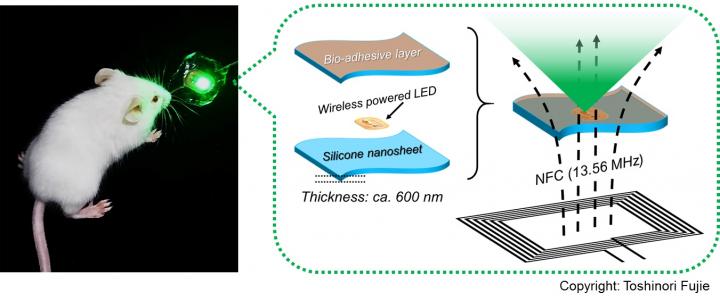
Scientists from Waseda University, the National Defense Medical College, and the Japan Science and Technology Agency developed a new bioadhesive, wirelessly-powered light-emitting device which could better treat cancers in delicate organs.
Conventional photodynamic therapy induces cancer cell death by using photosensitizing agents, which localize in tumors and activate with exposure to a specific wavelength of light. In recent years, low-dose and long-term photodynamic therapy (metronomic photodynamic therapy, mPDT) has shown promise in treating cancers in internal organs. The problem with mPDT is, however, is that because the light intensity is extremely low (1/1000 of the conventional method), the antitumor effect cannot be obtained if the light source shifts even slightly away from the tumor, making the illumination insufficient.
"To address this issue, we have developed a wirelessly-powered optoelectronic device that stably fixes itself onto the inner surface of an animal tissue like a sticker with bioadhesive and elastic nanosheets, enabling a continuous, local light delivery to the tumor," says Toshinori Fujie, associate professor of biomedical engineering at Waseda University. The nanosheets are modified with the mussel adhesive protein-inspired polymer polydopamine, which can stabilize the device onto a wet animal tissue for more than 2 weeks without surgical suturing or medical glue. The light-emitting diode chips in the device are wirelessly powered by near-field-communication technology.
To test its effectiveness, tumor-bearing mice implanted with the device were injected with a photosensitizing agent (photofrin) and exposed to red and green light, approximately 1,000-fold intensity lower than the conventional PDT approaches, for 10 consecutive days. The experiment showed that the tumor growth was significantly reduced overall. Especially under green light, the tumor in some mice was completely eradicated.
Associate Professor Fujie points out, "This device may facilitate treatment for hard-to-detect microtumors and deeply located lesions that are hard to reach with standard phototherapy, without having to worry about the risk of damaging healthy tissues by overheating. Furthermore, because the device does not require surgical suturing, it is suitable for treating cancer near major nerves and blood vessels, as well as for organs that are fragile, that change their shape, or that actively move, such as the brain, liver, and pancreas."
If clinically applied, the device could be beneficial for cancer patients who seek minimally invasive treatment, helping them live longer and improve their quality of life.
###
This study was published online in Nature Biomedical Engineering on July 16, 2018 (GMT).
Reference
Title: Tissue-adhesive wirelessly powered optoelectronic device for metronomic photodynamic cancer therapy
Author: Kento Yamagishi, Izumi Kirino, Isao Takahashi, Hizuru Amano, Shinji Takeoka, Yuji Morimoto & Toshinori Fujie
Published online in Nature Biomedical Engineering on July 16, 2018 (GMT)
DOI: 1038/s41551-018-0261-7
University news on this study
About Waseda University
Waseda University is a leading private, non-profit institution of higher education based in central Tokyo, enrolling over 50,000 students in the 13 undergraduate and 20 graduate schools. Founded in 1882, Waseda cherishes three guiding principles: academic independence, practical innovation and the education of enlightened citizens. Established to mold future leaders, Waseda continues to fulfill this mission, counting among its alumni seven prime ministers and countless other politicians, business leaders, journalists, diplomats, scholars, scientists, actors, writers, athletes and artists. The University is also number one in Japan in international activities, including the number of international students, and has the broadest range of degree programs fully taught in English.
Media Contact
Jasper Lam
[email protected]
@waseda_univ
Original Source
https://www.waseda.jp/top/en-news/60952 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0261-7