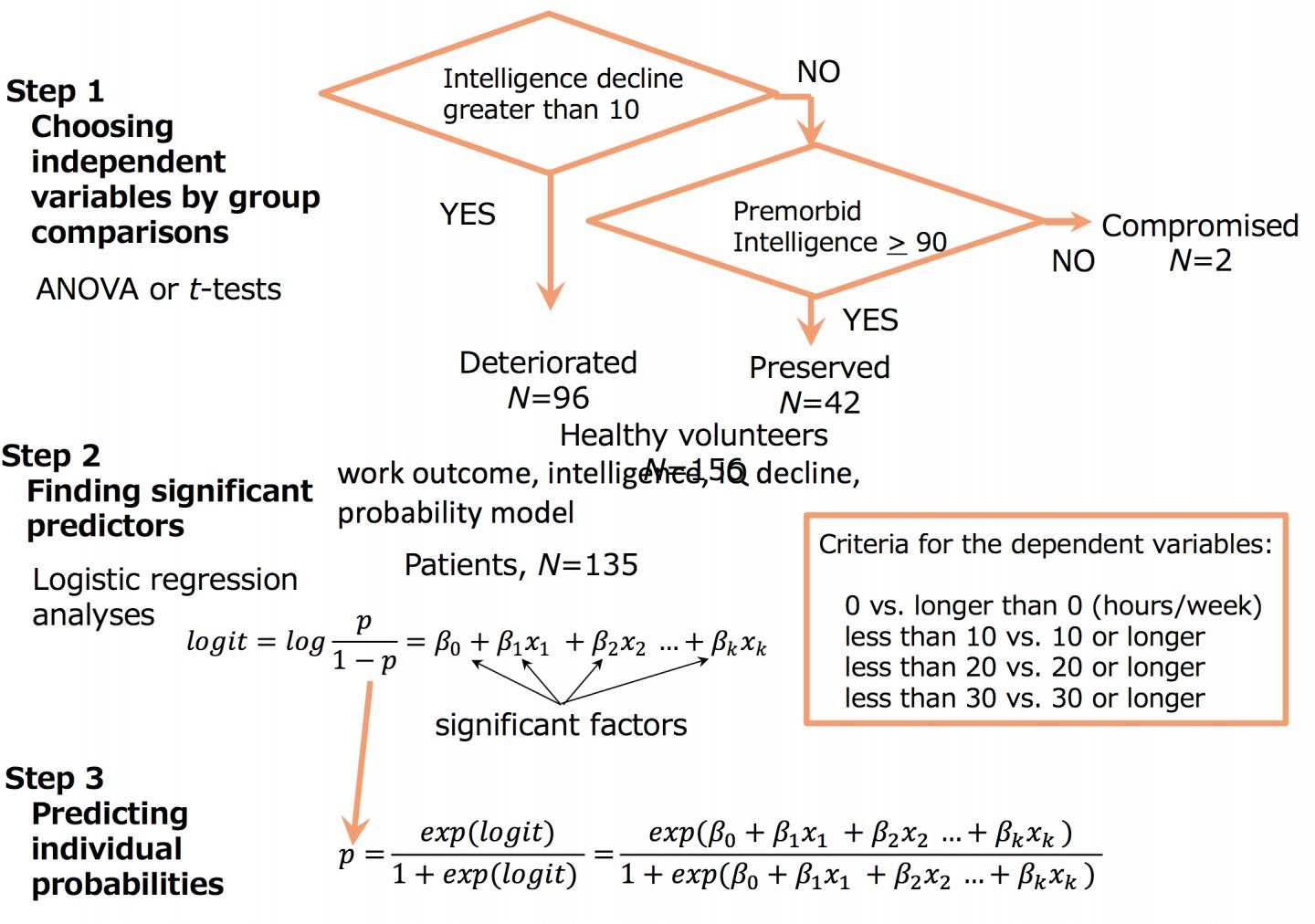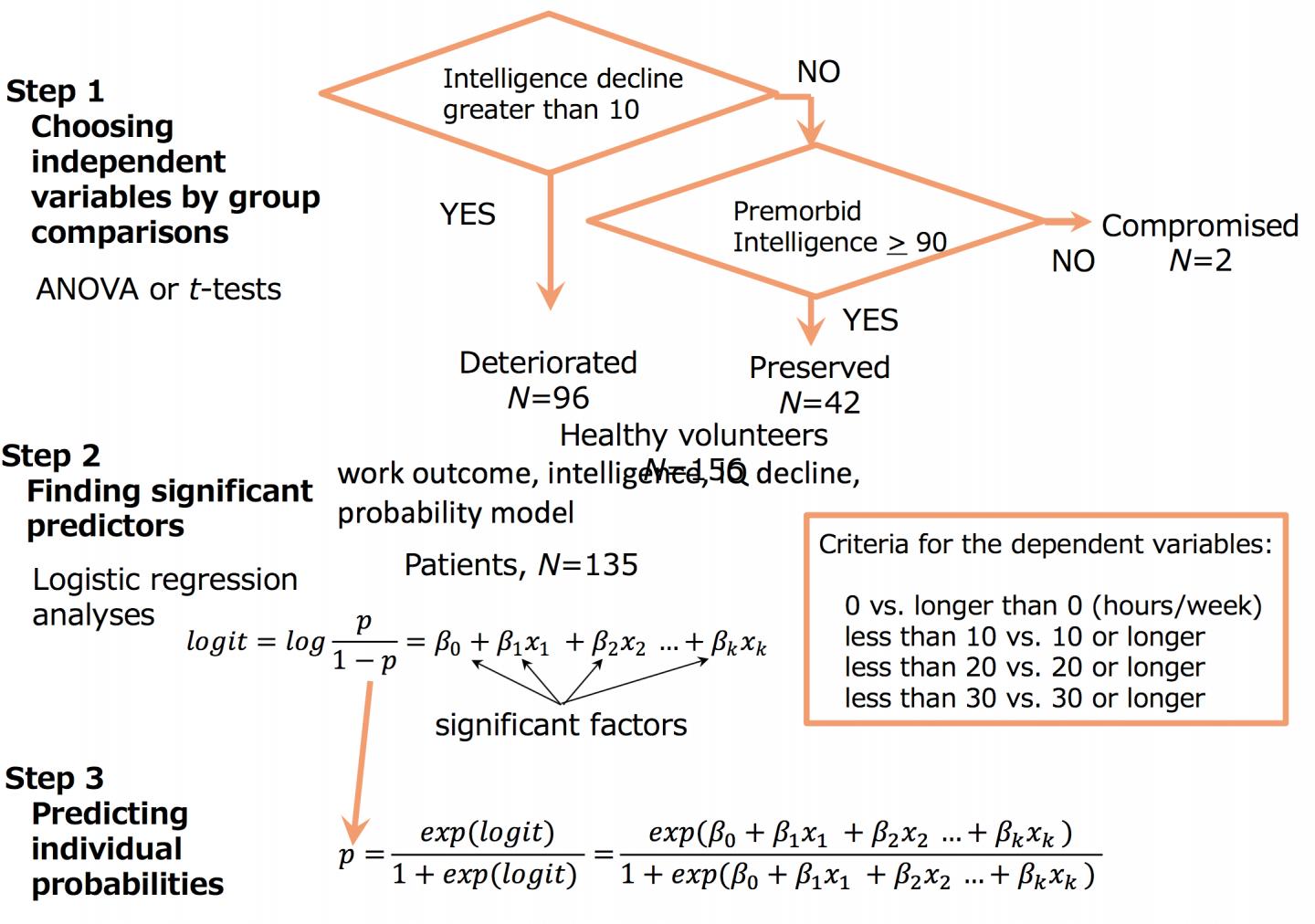
Credit: Sumiyoshi, C., et al., Schizophr. Res. (2018), DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2018.05.042
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder that occurs in one out of every 100 people. Its symptoms include positive symptoms, such as hallucinations and delusions, and negative symptoms, such as social withdrawal, apathy, and cognitive impairments. In many cases, these symptoms become chronic and relapse. In addition, many patients with schizophrenia show deterioration of intelligence, which prevents them from independent living in their community, and joining the work force, in particular.
A research team led by Ryota Hashimoto at Osaka University clarified that IQ decline, defined as a difference between current full scale IQ (FIQ) and estimated premorbid IQ, was related to work status in patients with schizophrenia. The researchers also proposed a method for estimating probabilities of work outcome in those patients based on related factors, such as IQ decline, social function, and psychiatric symptoms. Their research results were published in Schizophrenia Research.
First, various variables were compared between the preserved group (patients with preserved IQ), the deteriorated group (patients whose current intelligence was lower than their estimated premorbid intelligence), and the healthy controls (the group of healthy volunteers).
Next, they performed logistic regression analyses to predict work status in patients with schizophrenia using the significant variables found in the group comparisons. The work status was dichotomized by a criterion of 1, 10, 20, or 30 hours per week. At each criterion, patients were classified into either the above or the below criterion according to their actual work hours.
The analyses demonstrated that IQ decline was effective for predicting work status. Based on the equations obtained from the logistic regression models, they also presented a method for predicting probabilities for working longer than each criterion.
The first author Chika Sumiyoshi at Fukushima University says, "The amount of work performed by patients with schizophrenia was predicted by doctors only based on their experience and intuition. Our research results will help them to explain how many hours patients can work to them and their families based on objective data and promote consensus-building between the patient and physician. This will help motivate patients to receive treatment and promote their reintegration into society.
###
The article, "Predicting work outcome in patients with schizophrenia: Influence of IQ decline" was published in Schizophrenia Research, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2018.05.042.
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan's most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university's ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum.
Website: http://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en/top
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
@osaka_univ_e
http://www.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
Original Source
http://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en/research/2018/20180629_2 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2018.05.042