Credit: WSU
PULLMAN, Wash. – Washington State University researchers have created a sustainable alternative to traditional concrete using coal fly ash, a waste product of coal-based electricity generation.
The advance tackles two major environmental problems at once by making use of coal production waste and by significantly reducing the environmental impact of concrete production.
Xianming Shi, associate professor in WSU's Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, and graduate student Gang Xu, have developed a strong, durable concrete that uses fly ash as a binder and eliminates the use of environmentally intensive cement. They report on their work in the August issue of the journal, Fuel.
Reduces energy demand, greenhouse emissions
Production of traditional concrete, which is made by combining cement with sand and gravel, contributes between five and eight percent of greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. That's because cement, the key ingredient in concrete, requires high temperatures and a tremendous amount of energy to produce.
Fly ash, the material that remains after coal dust is burned, meanwhile has become a significant waste management issue in the United States. More than 50 percent of fly ash ends up in landfills, where it can easily leach into the nearby environment.
While some researchers have used fly ash in concrete, they haven't been able to eliminate the intense heating methods that are traditionally needed to make a strong material.
"Our production method does not require heating or the use of any cement," said Xu.
Molecular engineering
This work is also significant because the researchers are using nano-sized materials to engineer concrete at the molecular level.
"To sustainably advance the construction industry, we need to utilize the 'bottom-up' capability of nanomaterials," said Shi.
The team used graphene oxide, a recently discovered nanomaterial, to manipulate the reaction of fly ash with water and turn the activated fly ash into a strong cement-like material. The graphene oxide rearranges atoms and molecules in a solution of fly ash and chemical activators like sodium silicate and calcium oxide. The process creates a calcium-aluminate-silicate-hydrate molecule chain with strongly bonded atoms that form an inorganic polymer network more durable than (hydrated) cement.
Aids groundwater, mitigates flooding
The team designed the fly ash concrete to be pervious, which means water can pass through it to replenish groundwater and to mitigate flooding potential.
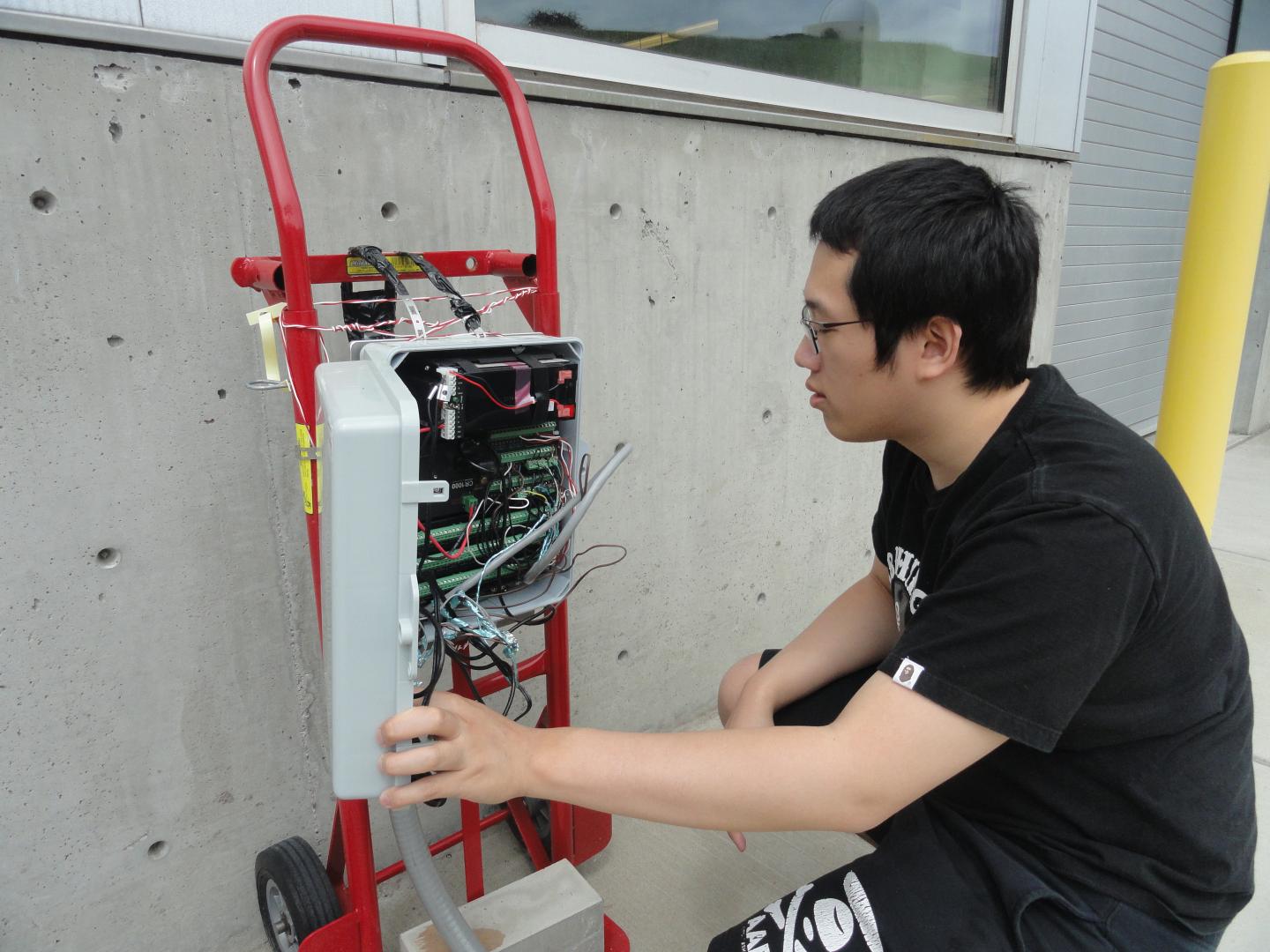
Researchers have demonstrated the strength and behavior of the material in test plots on the WSU campus under a variety of load and temperature conditions. They are still conducting infiltration tests and gathering data using sensors buried under the concrete. They eventually hope to commercialize the patented technology.
"After further testing, we would like to build some structures with this concrete to serve as a proof of concept," said Xu.
###
The research was funded by the U.S. Department of Transportation's University Transportation Centers and the WSU Office of Commercialization.
Media Contact
Xianming Shi
[email protected]
509-335-7088
@WSUNews
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.04.033