Credit: Riitta-Leena Inki
Electrospun sodium titanate speeds up the purification of water based on selective ion exchange – effectively extracts radio-active strontium
With the help of this new method, waste water can be treated faster than before, and the environmentally positive aspect is that the process leaves less solid radio-active waste.
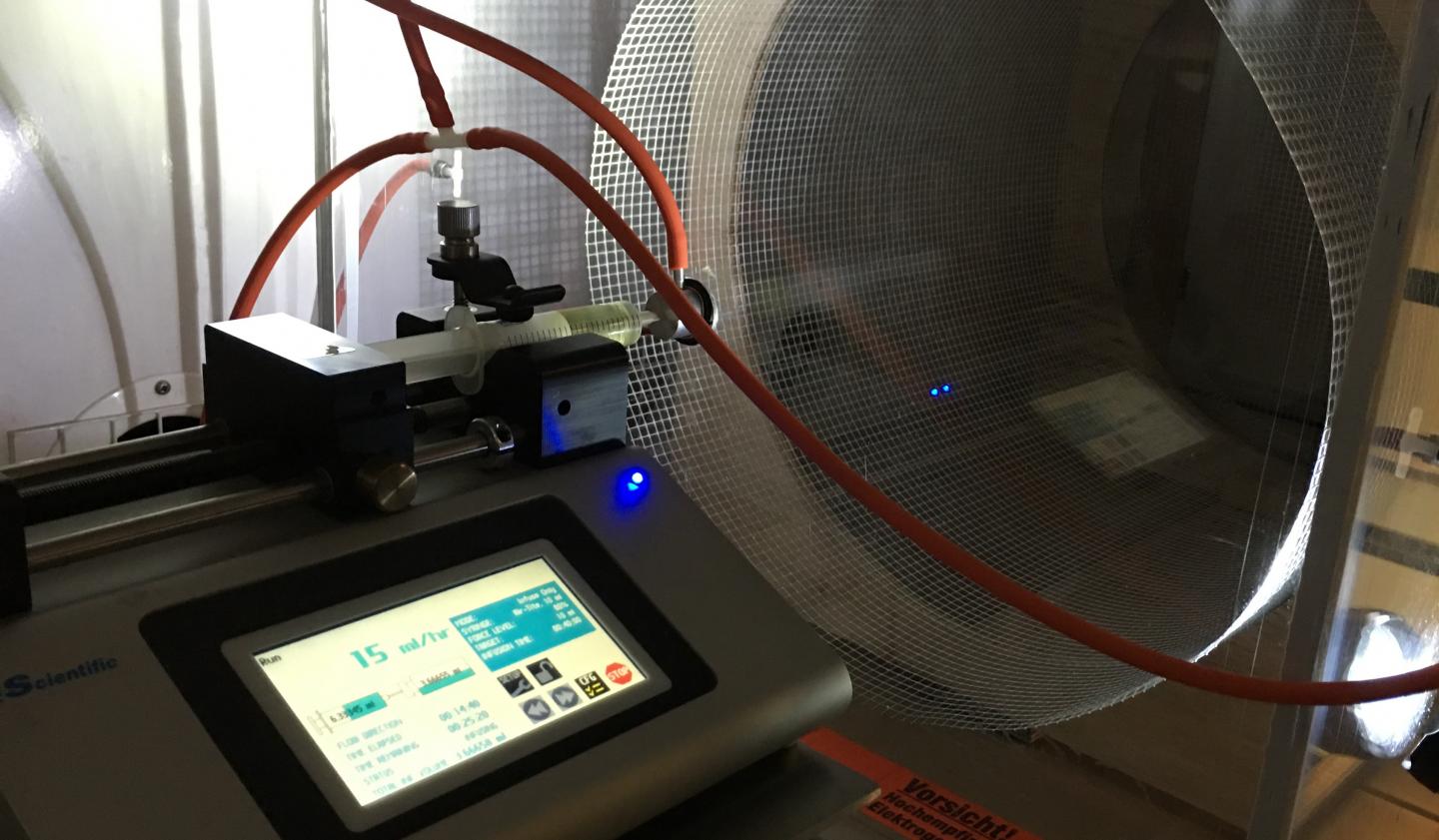
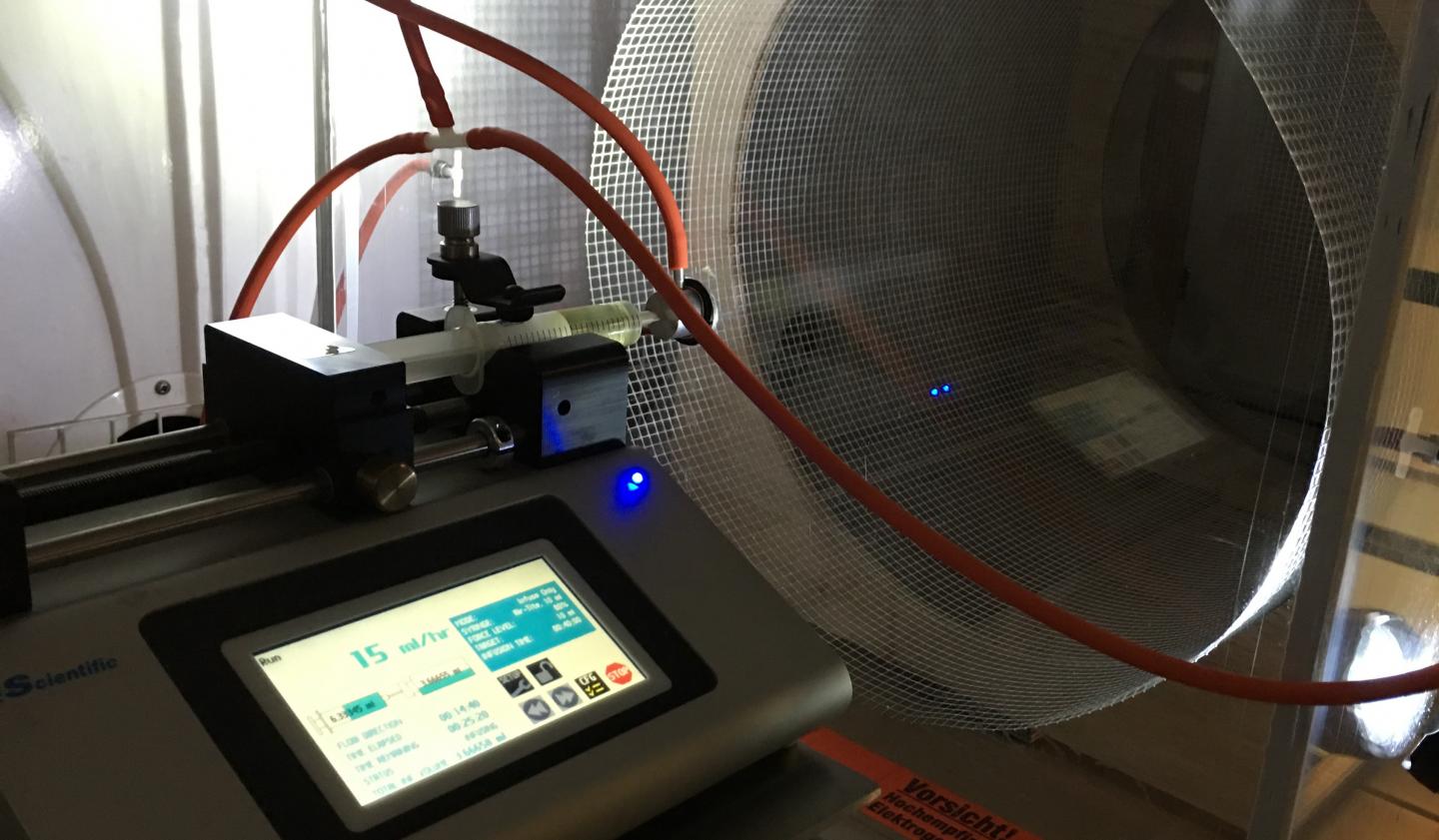
The properties of electrospun sodium titanate are equal to those of commercially produced ion-exchange materials.
– The advantages of electrospun materials are due to the kinetics, i.e. reaction speed, of ion exchange, says Risto Koivula, a scientist in the research group Ion Exchange for Nuclear Waste Treatment and for Recycling at the Department of Chemistry at the University of Helsinki.
Synthetic sodium titanate is known as an effective remover of strontium, and granular sodium titanate is used in industrial quantities.
The purging method based on ion exchange was originally developed by Jukka Lehto and Risto Harjula from the University of Helsinki.
At present, granular sodium titanate is used to purify e.g. the waste water from the Fukushima nuclear disaster.
As it is run through an ion exchanger loaded into column, the radio-active strontium in the water is changed into sodium.
When the ion exchange capacity is filled, the filtering material has to be switched out. This leaves some solid radio-active waste.
– Since less electrospun material is needed from the start of the process, the radio-active waste requiring a permanent repository will also fit in a smaller space, says Koivula.
The electrospinning equpiment at the University of Helsinki was developed and built in the centre of excellence for atomic layer deposition, led by Mikko Ritala. The researchers successfully tried this quite simple method for working sodium titanate into fibre. Koivula's team studied the ion exchange features of fibre produced this way and found it worked like the commercially produced ones.
###
More details:
Researcher Risto Koivula, Ion exchange for nuclear waste treatment and for recycling research group, University of Helsinki, email: [email protected], Phone: + 358 50 4486640
Media Contact
Riitta-Leena Inki
[email protected]
358-504-485-770
@helsinkiuni
http://www.helsinki.fi/university/
Original Source
https://www.helsinki.fi/en/news/science/electrospun-sodium-titanate-speeds-up-the-purification-of-water-based-on-selective-ion-exchange-effectively-extracts-radio-active-strontium http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1481888