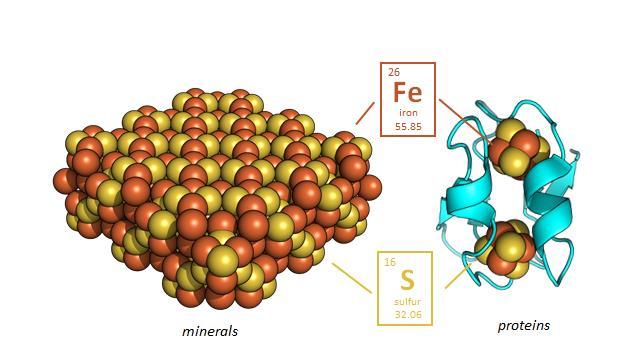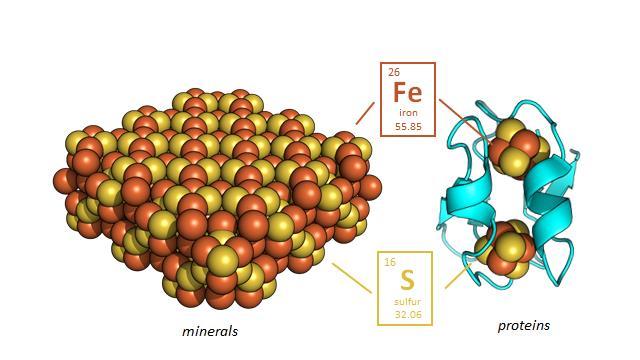
Credit: Professor Vikas Nanda/Center for Advanced Biotechnology and Medicine at Rutgers
What are the origins of life on Earth and possibly elsewhere? Did "protein nanomachines" evolve here before life began to catalyze and support the development of living things? Could the same thing have happened on Mars, the moons of Jupiter and Neptune, and elsewhere in the universe?
A Rutgers University-led team of scientists called ENIGMA, for "Evolution of Nanomachines in Geospheres and Microbial Ancestors," will try to answer those questions over the next five years, thanks to an approximately $6 million NASA grant and membership in the NASA Astrobiology Institute.
Rutgers Today asked Paul G. Falkowski, ENIGMA principal investigator and a distinguished professor at Rutgers University-New Brunswick, about research on the origins of life.
What is astrobiology?
It is the study of the origins of life on Earth and potential life on planets – called extrasolar planets – and planetary bodies like moons in our solar system and other solar systems. More than 3,700 extrasolar planets have been confirmed in the last decade or so. Many of these are potentially rocky planets that are close enough to their star that they may have liquid water, and we want to try and understand if the gases on those planets are created by life, such as the oxygen on Earth.
What is the ENIGMA project?
All life on Earth depends on the movement of electrons; life literally is electric. We breathe in oxygen and breathe out water vapor and carbon dioxide, and in that process we transfer hydrogen atoms, which contain a proton and an electron, to oxygen to make water (H20). We move electrons from the food we eat to the oxygen in the air to derive energy. Every organism on Earth moves electrons to generate energy. ENIGMA is a team of primarily Rutgers researchers that is trying to understand the earliest evolution of these processes, and we think that hydrogen was probably one of the most abundant gases in the early Earth that supported life.
What are the chances of life being found elsewhere in our solar system and the universe?
We've been looking for evidence of life on Mars since the Viking mission, which landed in 1976. I think it will be very difficult to prove there is life on Mars today, but there may be signatures of life that existed on Mars in the distant past. Mars certainly had a lot of water on it and had an atmosphere, but that's all largely gone now. A proposed mission to Europa – an ice-covered moon of Jupiter – is in the planning phase. NASA's Cassini mission to investigate Titan, a moon of Neptune, revealed liquid methane over what we think is water – very cold, shallow oceans – so there may be life on Titan.
What are protein nanomachines?
They are enzymes that physically move. Each time we take a breath, an enzyme in every cell allows you to transfer electrons to oxygen. Enzymes, like all proteins, are made up of amino acids, of which there are 20 that are used in life. Early on, amino acids were delivered to Earth by meteorites, and we think some of these amino acids could have been coupled together and made nanomachines before life began. That's what we're looking to see if we can recreate, using the tens of thousands of protein structures in the Protein Data Bank at Rutgers together with our colleagues in the Center for Advanced Biotechnology and Medicine.
What are the next steps?
Organizing our research so it is coherent and relevant to the other collaborating teams in the NASA Astrobiology Institute. We want to develop an education and outreach program at Rutgers that leads to an astrobiology minor for undergraduate students and helps inform K-12 schoolchildren about the origins of life on Earth and what we know and don't know about the potential for life on other planets. We also want to help make Rutgers a center of excellence in this field so future undergraduate and graduate students and faculty will gravitate towards this university to try to understand the evolution and origin of the molecules that derive energy for life.
###
Media Contact
Todd Bates
[email protected]
848-932-0550
@RutgersU
http://www.rutgers.edu
Original Source
https://news.rutgers.edu/nasa-funds-rutgers-scientists%E2%80%99-pursuit-origins-life/20180601#.WxGTye4vy70