Credit: Professor Sumio Ohtsuki
Intestinal bacteria have attracted recent attention since they were discovered to influence various physiological functions and diseases in humans. Researchers from Kumamoto University in Japan analyzing the influence of changes in intestinal bacteria on sugar and lipid metabolism have found that secondary bile acids produced by the bacteria can influence blood glucose and lipid concentrations as well as parts of their molecular mechanisms. This result is expected to lead to the treatment of metabolic diseases such as diabetes and dyslipidemia by targeting intestinal bacteria that produce secondary bile acid.
More than 100 trillion bacteria from an estimated 1,000 different species inhabit our intestines. It has been reported that the profiles of intestinal bacteria in obese and non-obese people tend to be different and involved with the health of the host. The bacteria may affect energy consumption and fat accumulation of host body. In addition, it is known that these bacteria are also associated with lifestyle diseases such as type 2 diabetes, nervous diseases such as autism, and intestinal diseases such as colon cancer.
One factor that alters intestinal bacteria is the administration of antimicrobials. It is becoming clear that these drugs cause dysbiosis in the qualitative and quantitative balance of bacterial populations in the intestine and have various effects on vital functions. For example, hypoglycemia is a serious, but rare, side effect of antibiotics. In fact, some antibiotics, such as gatifloxacin, have been discontinued due to their side effects. Furthermore, taking antibiotics in infancy or childhood has been reported to accelerate weight gain.
Previous research has shown that dysbiosis due to antibiotic administration influences protein expression levels in the liver, an organ responsible for sugar and lipid metabolism. Thus, researchers at Kumamoto University decided to clarify the influence of antibiotic-caused dysbiosis on sugar and lipid metabolism and the mechanism thereof.
[Result]
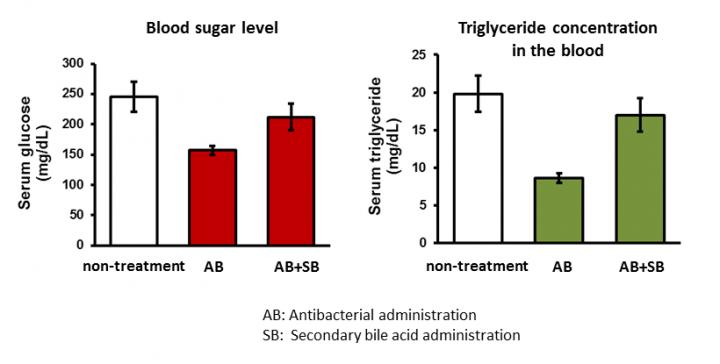
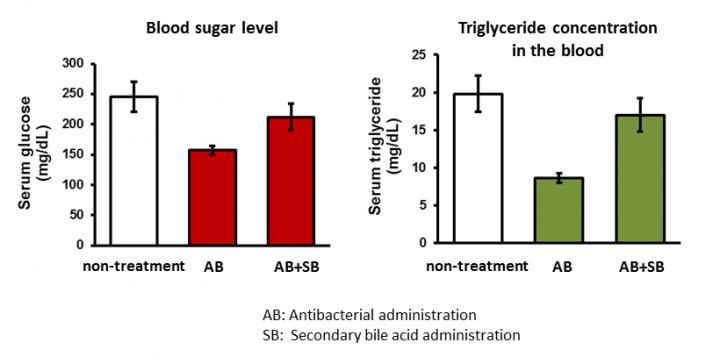
A dysbiosis mouse model was prepared by administering antibiotics for 5 days. Compared to non-antibiotic treated mice, the blood glucose levels and lipid (triglyceride) concentrations in the experimental model decreased to 64% and 43% respectively. To assess the mechanisms related to these reductions, researchers focused on secondary bile acids. These acids are metabolites produced by intestinal bacteria that control the liver functions involved in sugar and lipid metabolism.
In the experimental mouse model, intestinal bacteria producing secondary bile acids decreased. Additionally, the concentrations of secondary bile acids (lithocholic and deoxycholic acid) in the mouse liver were reduced to 20% and 0.6% respectively compared to non-antibiotic treated mice. When secondary bile acid is supplemented at the same time as antibiotic administration, blood glucose and blood triglyceride levels recovered. This result indicates that the secondary bile acid produced by intestinal bacteria affects sugar and lipid metabolism of the host.
Next, the researchers used quantitative proteomics to comprehensively analyze the amount of proteins to assess how secondary bile acids produced by intestinal bacteria influence liver sugar and lipid metabolism. In the livers of the dysbiosis mouse model, the expression levels of proteins involved in glycogen metabolism (storage of sugar) and in the biosynthesis of cholesterol and bile acids were found to have changed. Moreover, the change was restored through supplementation of secondary bile acids.
"Our research shows that enterobacteria and the secondary bile acids that they produce may be involved in the change of concentration of sugars and lipids in living bodies," said Kumamoto University Professor Sumio Ohtsuki, leader of the study. "It is expected that these bacteria will be a future target for the prevention or treatment of metabolic diseases such as diabetes or dyslipidemia."
This research result was posted online in the journal Scientific Reports on 19 January 2018.
###
[Source]
Kuno, T., Hirayama-Kurogi, M., Ito, S., & Ohtsuki, S. (2018). Reduction in hepatic secondary bile acids caused by short-term antibiotic-induced dysbiosis decreases mouse serum glucose and triglyceride levels. Scientific Reports, 8(1). doi:10.1038/s41598-018-19545-1
Media Contact
J. Sanderson & N. Fukuda
[email protected]
http://ewww.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/en/news/
Original Source
http://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-19545-1 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19545-1