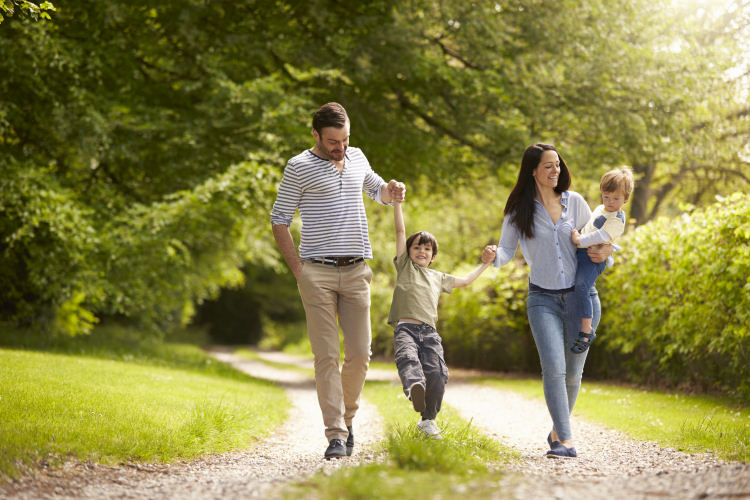
A new study concludes that walking has the potential to significantly improve the public’s health. It finds regular walking, even if not meeting the minimum recommended levels, is associated with lower mortality compared to inactivity. The study appears early online in American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Public health guidelines recommend adults engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week. But surveys show only half of U.S. adults meet this recommendation. Older adults are even less likely to meet minimum recommendations (42% ages 65-74 years and 28% ages 75 years and older).
Walking is the most common type of physical activity, and has been associated with lower risk of heart disease, diabetes, and breast and colon cancers. While several studies have linked overall moderate-vigorous physical activity to a reduced risk of death, relatively few have examined associations with walking specifically.
To learn more, investigators led by Alpa Patel, Ph.D., looked at data from nearly 140,000 participants in the Cancer Prevention Study II Nutrition Cohort. A small percentage (6-7%) in the study reported no moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity at baseline. Among the rest, about 95% reported some walking, and nearly half walked as their only form of moderate-vigorous physical activity.
After correcting for other risk factors, including smoking, obesity, and chronic conditions, the study found walking-only for less than 2 hours per week was associated with lower all-cause mortality compared to no activity. Meeting 1 to 2 times the minimum recommendation (2.5-5 hours/week) through walking-only was associated with 20% lower mortality risk. Results for those exceeding recommendations through walking-only were similar to those who met recommendations.
Walking-only was most strongly associated with respiratory disease mortality, with approximately 35% lower risk comparing more than 6 hours/week of walking to the least active group. Walking-only was also associated with about 20% less risk of cardiovascular disease mortality and with about 9 percent less risk of cancer mortality.
“Walking has been described as the ‘perfect exercise’ because it is simple, free, convenient, doesn’t require any special equipment or training, and can be done at any age,” said Dr. Patel. “With the near doubling of adults aged 65 and older expected by 2030, clinicians should encourage patients to walk even if less than the recommended amount, especially as they age, for health and longevity.”
###
Article: Patel AV, Hildebrand JS, Leach CR, et al. Walking in relation to mortality in a large prospective cohort of older U.S. adults. Am J Prev Med. 2017 [in press] DOI: 10.1016/j.amepre.2017.08.019.
Media Contact
David Sampson
[email protected]
@ACSNews
http://www.cancer.org