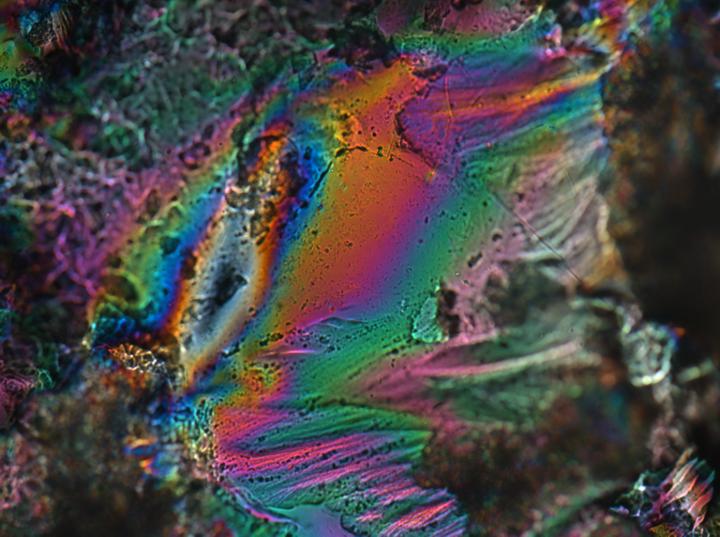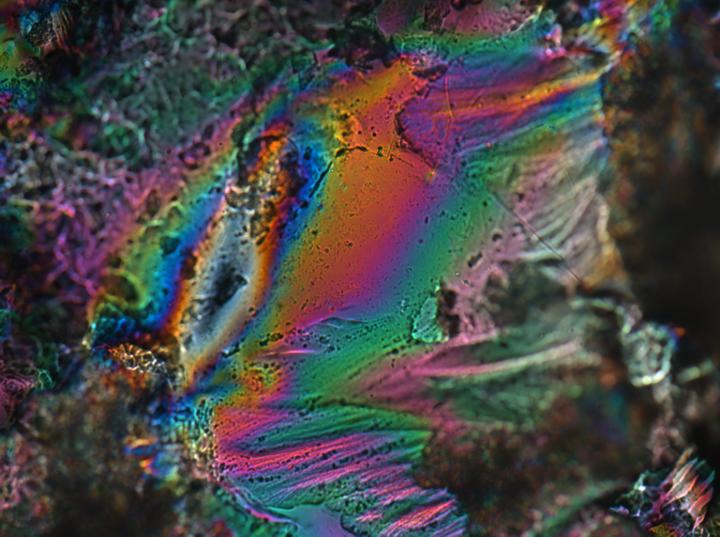
IMAGE: The liquid crystalline hydrogel in a dry state.
Credit: Patrick Mather
Researchers, particularly those in the medical field, have been searching for a way to combine the properties of liquid crystallinity with those of hydrogels.
Liquid crystals are characterized as having the fluidity of liquid but some of the order of a crystal so they can be oriented to have structure. They are not water-loving, in that they will dissolve in water, making them less than ideal candidates for use inside the body.
Hydrogels, however, are water-loving but they lack the order to orient them into specific shapes.
Combining the properties of liquid crystals and hydrogels in just the right proportions creates the potential for new materials that have the same mechanical properties as soft tissues in the body. A material that is water-loving and has structure opens up the door the possibility for artificial blood vessels that are mechanically stealth so they wouldn't be viewed as a foreign body.
Professor Pat Mather has developed a process that can create this type of a polymer.
The paper "A hydrogel-forming liquid crystalline elastomer exhibiting soft shape memory" authored by Mather and graduate student Amir Torbati G'14, now a post-doc at UC Denver, was featured on the cover the Journal of Polymer Science B: Polymer Physics.
"It is a balancing act of not having too many water-loving groups in the polymer and balancing that with other chemicals in the polymer that promote structure." said Mather.
Whatever the hydrogels do to make the liquid crystals water-loving destroys the order of crystallinity, so historically creating a material like this has been a challenge but Mather's process opens to the door to new medical applications that were previously out of reach.
###
To see the full article visit: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/polb.v54.1/issuetoc
Media Contact
Ariel Duchene
[email protected]
315-443-2546
http://www.syr.edu