Credit: Saba Parween
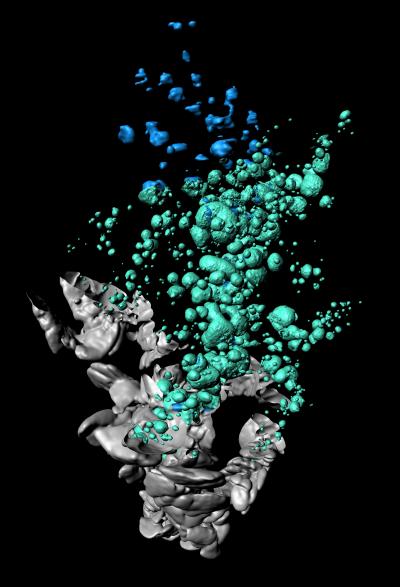
Researchers at the Umeå Center for Molecular Medicine have created the first 3D spatial visualization of an obese mouse pancreas showing the distribution dynamics of insulin producing beta cells. The results show significant amounts of cystic lesions within pancreatic islets. These lesions could be linked to alterations in the mass and function of insulin producing beta cells.
"By using the method optical projection tomography (OPT), we created the first 3D-spatial and quantitative account of beta cell mass distribution in an obese and insulin resistant mouse model," says Saba Parween, researcher at the Umeå Center for Molecular Medicine.
The 3D-depiction revealed a previously unreported degree of cystic lesions in large islets that were occupied by red blood cells and fibrin mesh. According to Saba Parween, these lesions could be caused by a mechanism involving the leakage of red blood cells and blood plasma due to increased blood flow and vessel instability within the islets. Intra-islet lesions have apparently been overlooked in the past.
The pancreatic endocrine cells, most importantly the insulin producing beta cells, play an important role in regulating blood glucose homeostasis. Alterations in the beta cell mass or the function of the insulin producing cells play a major role in the development and progression of diabetes.
"Understanding beta cell mass dynamics in disease models is therefore a key aspect for better interpretation of research results. More in depth studies will be required to address the potential effects of these cystic lesions on beta cell function," says Saba Parween.
The data also indicated that different lobes of the pancreas have different potential for expanding their beta cell mass. The observed variations in beta cell mass expansion suggest that a careful consideration of these variations is required while performing tissue sampling for studying diabetes disease dynamics.
The possibility to monitor beta cell mass in vivo would radically improve researcher's abilities to study the pathogenesis of diabetes and potentially also the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is a widely used technique that has become a promising approach to monitor changes in beta cell mass in vivo. A key issue for using this approach is to evaluate the beta cell specificity and read out of the utilized radiotracers. This is most commonly performed by conventional stereological approaches, which rely on the extrapolation of 2D data.
"Therefore, we developed a new OPT-based multimodal imaging protocol that enables rapid and accurate cross evaluation of radiotracers for SPECT-based beta cell imaging. We propose that this protocol is an accurate and better approach for validating the performance radiotracers for beta cell imaging," concludes Saba Parween.
###
Saba Parween is a molecular biologist from India working on imaging beta cells during diabetes by using optical projection tomography. She has been a Marie Curie research fellow in the BetaTrain consortium, did her secondment at R&D site of Novo Nordisk in Copenhagen for a month and had a collaboration with Radboud Universuity Nijmegen Medical Centre (RUNMC) during her PhD in Molecular Medicine. Before starting her PhD in 2012, she earned her Master's in Biotechnology in 2010 and then worked at National Brain Research Centre in India.
For more information, please contact:
Saba Parween, Umeå Center for Molecular Medicine
Phone: 090-785 4419
Email: [email protected]
Media Contact
Daniel Harju
[email protected]
46-725-522-918
@UmeaUniversity
http://www.umu.se/umu/index_eng.html