Scientists have discovered that a specialised white blood cell found in birds can destroy a potentially fatal fungal infection which affects more than one million people every year.
Cryptococcus neoformans is a fungus that causes fatal infections in those with a weakened immune system. It is one of the most dangerous infections of individuals with AIDS and is thought to cause hundreds of thousands of deaths worldwide, every year.
Birds are known to carry the fungus and their droppings are thought to be a source of human infection; however it has been a longstanding mystery why the birds themselves do not appear to become ill.
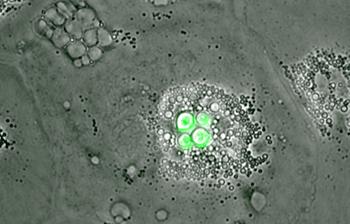
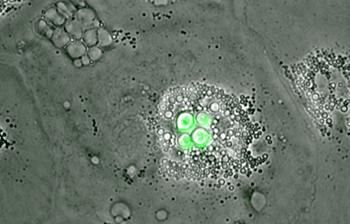
Now, a team from the University of Sheffield have shown that a particular white blood cell within the bird's blood system, called a macrophage, is able to completely block the growth of Cryptococci.
The scientists, led by Dr Simon Johnston, found that the fungus can grow slowly within the bird's digestive tract, but if it tries to invade the bird's body then the immune system immediately destroys it – which explains why healthy birds can still help spread the infection.
Dr Johnston said: "Birds have a higher body temperature than humans, 42 o C instead of 37 o C, but this alone is not enough to fully stop the fungus.
"By studying bird cells under the microscope, we have seen that macrophage cells have the ability to completely block the growth of the fungus, which can be fatal in humans.
"Understanding where the disease comes from and how it spreads is critical. If we can learn how some animals are able to resist infection we might be able to gain insights into how we can improve the human immune response to this fungus."
This work, published in Scientific Reports, was carried out in collaboration with the University of Birmingham and is part of a much larger international effort to understand, fight and ultimately eliminate cryptococcosis.
Dr Johnston added: "We are now working with leading scientists from all over the world to try and understand where this pathogen came from, how our bodies fight it and what we can do to help our own immune system defend us from this fungus and other related infections.
"Many human diseases are spread by birds, but we know surprisingly little about their immune systems. Discovering how they resist otherwise fatal infections offers the hope of improving our ability to intervene in this cycle and prevent a diverse range of human diseases."
He added: "In addition, infectious diseases of birds themselves are a major threat to agriculture, such as when 170,000 poultry were culled due a suspected bird flu outbreak.
"Learning more about the bird immune system is an important step in developing new ways to combat such infections."
###
The work was funded by the Medical Research Council, Lister institute for Preventative Medicine and all of the authors are members of the Wellcome Trust Strategic Award for Medical Mycology and Fungal Immunology, a pan-UK consortium supported by the Wellcome Trust that provides funding to link research groups in medical mycology together across the UK.
Notes to Editors
To view the full paper please visit: DOI: 10.1038/srep20977
The University of Sheffield
With almost 27,000 of the brightest students from over 140 countries, learning alongside over 1,200 of the best academics from across the globe, the University of Sheffield is one of the world's leading universities.
A member of the UK's prestigious Russell Group of leading research-led institutions, Sheffield offers world-class teaching and research excellence across a wide range of disciplines.
Unified by the power of discovery and understanding, staff and students at the university are committed to finding new ways to transform the world we live in.
In 2014 it was voted number one university in the UK for Student Satisfaction by Times Higher Education and in the last decade has won four Queen's Anniversary Prizes in recognition of the outstanding contribution to the United Kingdom's intellectual, economic, cultural and social life.
Sheffield has five Nobel Prize winners among former staff and students and its alumni go on to hold positions of great responsibility and influence all over the world, making significant contributions in their chosen fields.
Global research partners and clients include Boeing, Rolls-Royce, Unilever, AstraZeneca, Glaxo SmithKline, Siemens and Airbus, as well as many UK and overseas government agencies and charitable foundations. For further information, please visit http://www.sheffield.ac.uk
For further information please contact: Amy Pullan, Media Relations Officer, University of Sheffield, 0114 222 9859, [email protected]
To read other news releases about the University of Sheffield, visit http://www.sheffield.ac.uk/news
Media Contact
Amy Pullan
[email protected]
01-142-229-859
@sheffielduni
http://www.shef.ac.uk