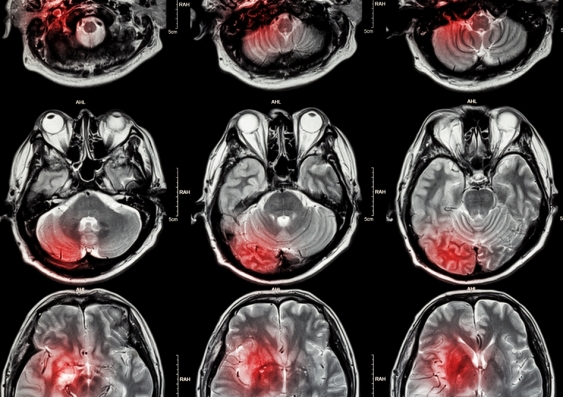
UNSW researchers have identified a promising new avenue to explore in the search for stroke treatments, after translating findings from Alzheimer’s disease. The study published in Nature Communications finds that mice deficient in tau, a protein within brain cells (neurons), are significantly protected from excitotoxic brain damage after experimental stroke.
Stroke is a major cause of death and disability, and there is only a short window for therapeutic intervention, aimed at restoring blood flow to the brain before neurons are irreversibly damaged.
Professor Lars Ittner and Dr Yazi Ke at UNSW and NeuRA had already established that in Alzheimer’s disease, memory deficits and early deaths were tau-dependent.
The researchers suspected a reduction of tau would also reduce acute brain damage in stroke.
“Tau as a drug target is intensively explored in Alzheimer’s disease, but as a drug target in stroke is completely new thinking,” Professor Ittner says.
“That’s where our paper has implications beyond mouse model molecular work. Drug development in this space should consider stroke as a disease that you can treat by targeting tau,” Dr Ke added.
The paper, with first author Dr Mian Bi and co-senior author Dr Ke, is the first to show a direct role of tau in brain damage after stroke. It demonstrates profound protection from brain damage, of more than 90 per cent, in the absence of tau.
Tau has been eyed as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease for several years, and Professor Ittner is hopeful that work in that area can also advance research on stroke.
But he cautions these findings were made in mouse models only, and that pathways to therapies take decades.
“This cannot yet be directly translated to therapy, but what it opens up is a new kind of thinking about the mechanisms that lead to brain damage after stroke, and as such, opens new avenues to develop therapies in the future,” he says.
Dr Bi says it will be important that other studies validate the work, and he is sure the findings will encourage more research in this direction.
“Around 10 years ago the drug development field in stroke was very hot, but most therapeutic stroke trials came to an end in failure,” he says.
“Avenues to therapy are very long, but this might re-start interest in the field with a new direction that hasn’t been tried before. It’s a bit of light after all the past failure.”
Professor Ittner agrees: “It’s a new insight into a disease that is at the molecular level, still poorly understood, and it needs such new insights or rethinking to make a step forward towards therapy.”
###
Media Contact
Gabrielle Dunlevy
[email protected]
61-293-851-933
@UNSWnews
http://www.unsw.edu.au
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00618-0