Credit: Anastasiia Garanina
Researchers from Lomonosov MSU Faculty of Biology have studied the stages of entosis, a process of cell death when one cell invades the other and gets digested inside of it. Entosis could become a new method of destroying cancer cells. The research was conducted as a part of the Noah's Ark Project, with the results published in the Scientific Reports.
Entosis is one of the variants of programmed cell death, or one of the types of cellular cannibalism. The process consists of one cell absorbing another and getting destroyed in it. Any cell that can attach to another cell can engage in entosis. Tumor cells do it most often, and can consume both similar and healthy cells. Scientists think that with the help of entosis it could be possible, on the contrary, to destroy those cancer cells that are resistant to drugs that cause apoptosis, which is another variant of programmed death, in which the cell simply breaks up into separate apoptotic bodies.
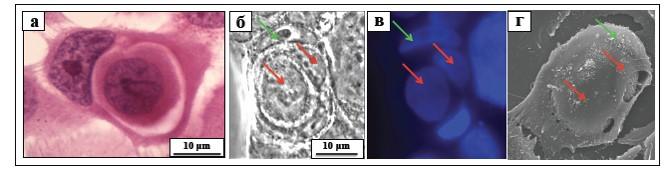
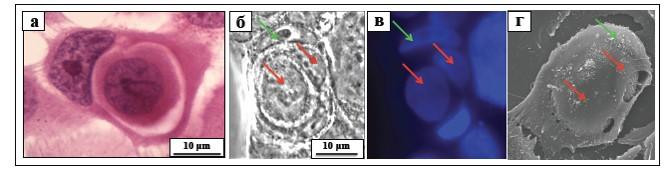
The consuming (entotic) cell forms an outgrowth of the plasma membrane – a special fold that "covers" the invading cell. Then the plasma membrane "collapses" along the fold, so that the invading cell is placed inside the entotic vacuole, where it is held by specialized structures – desmosomes. Soon, the membrane from which the vacuole consists begins to change: desmosome proteins disappear, and their place gets taken by proteins that are needed to merge with lysosomes – the organelles which will then "digest" the invading cell. The lysosomes of the entotic cell merge with the vacuole membrane, and digestive enzymes enter the vacuole to destroy the invading cell. Inside the invading cell, too, lysosomes are activated and grow in number. As a result, the invading cell collapses and dies. The products that are formed during the splitting of proteins, DNA, lipids, polysaccharides and other molecules of the implanted cell can serve as an additional food for the entotic cell.
The authors have found that the process of entosis consists of five consecutive stages. Transitions from one stage to another are accompanied by changes in the geometric forms of entotic and embedded cells and of some membrane organelles (Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes). The scientists distinguished the stages according to the shape of the inner cell, the structure of its nucleus and the state of the cytoplasm of both cells.
The authors have also showed that the Golgi apparatus, the microtubule cytoskeleton and actin microfilaments (threads made from the protein called actin that are present in all eukaryotic cells) play an important role in the realization of the entosis program. It has been proved that the experimental destruction of these three components inhibits the invasion of one cell into another, but does not stop the degradation of an already embedded cell. This means that these components do not participate in the final stages of entosis. This way of death of one cell inside another works in substrate-dependent cultures – in cells that grow and divide in culture only when they come into contact with a dense surface, such as glass or plastic.
"We have demonstrated that entosis is possible not only when the cells grow in a suspended state in a liquid medium, but also when they are attached to the substrate and to each other. We also were the first to discover that this process is stadial and that certain stages can be influenced," said one of the authors of the article, Galina Onishchenko, Doctor of Biology, Head of the Department of Cell Biology and Histology, Faculty of Biology, Lomonosov Moscow State University.
In the course of the work, the scientists cultivated the cells and conducted their vital monitoring. They used immunocytochemical and cytochemical staining to isolate the entotic cells, and observed them using video microscopy, light, fluorescence and confocal microscopy, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, and correlation microscopy.
In tumors, cells tend to be in close contact with each other. Evidence that entosis is possible both in cells interacting with each other and with the substrate, as well as understanding of the way in which one cell invades another are needed to scientists so that they can search for chemotherapeutic influences that induce entosis. This is important in cases where tumor cells are resistant to drugs that cause apoptosis. The authors note that they continue to investigate the phenomenon of entosis under different chemotherapeutic effects. This will allow in the future to understand the contribution that entosis makes to strengthening of tumor progression processes and to the development of tumor cells' resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs.
"The results of the research show that the stages of entosis involve successive changes in the various structural and functional characteristics both of the entotic and the invading cells. This allows us in the future to determine the mechanisms of transition from one stage of entosis to another and to find ways to control this variant of programmed cell death," Galina Onishchenko concluded.
The research was conducted in collaboration with scientists from the National Cancer Institute (USA).
###
Media Contact
Yana Khlyustova
[email protected]
http://www.msu.ru
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12867-6