Credit: Yale University
Scientists have spent decades studying the nature of tumor cells, but few have looked to see what was happening in the surrounding tissue.
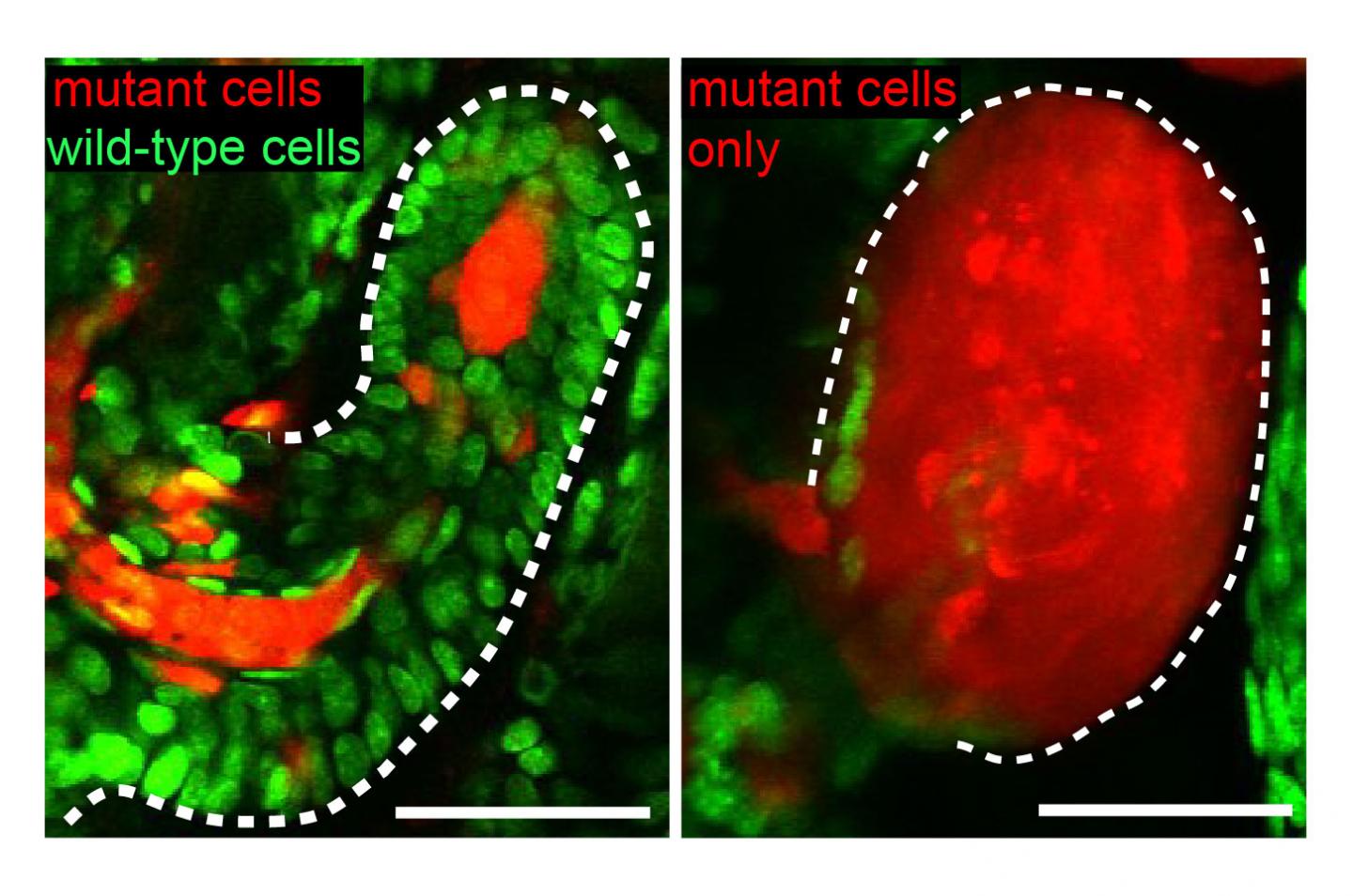
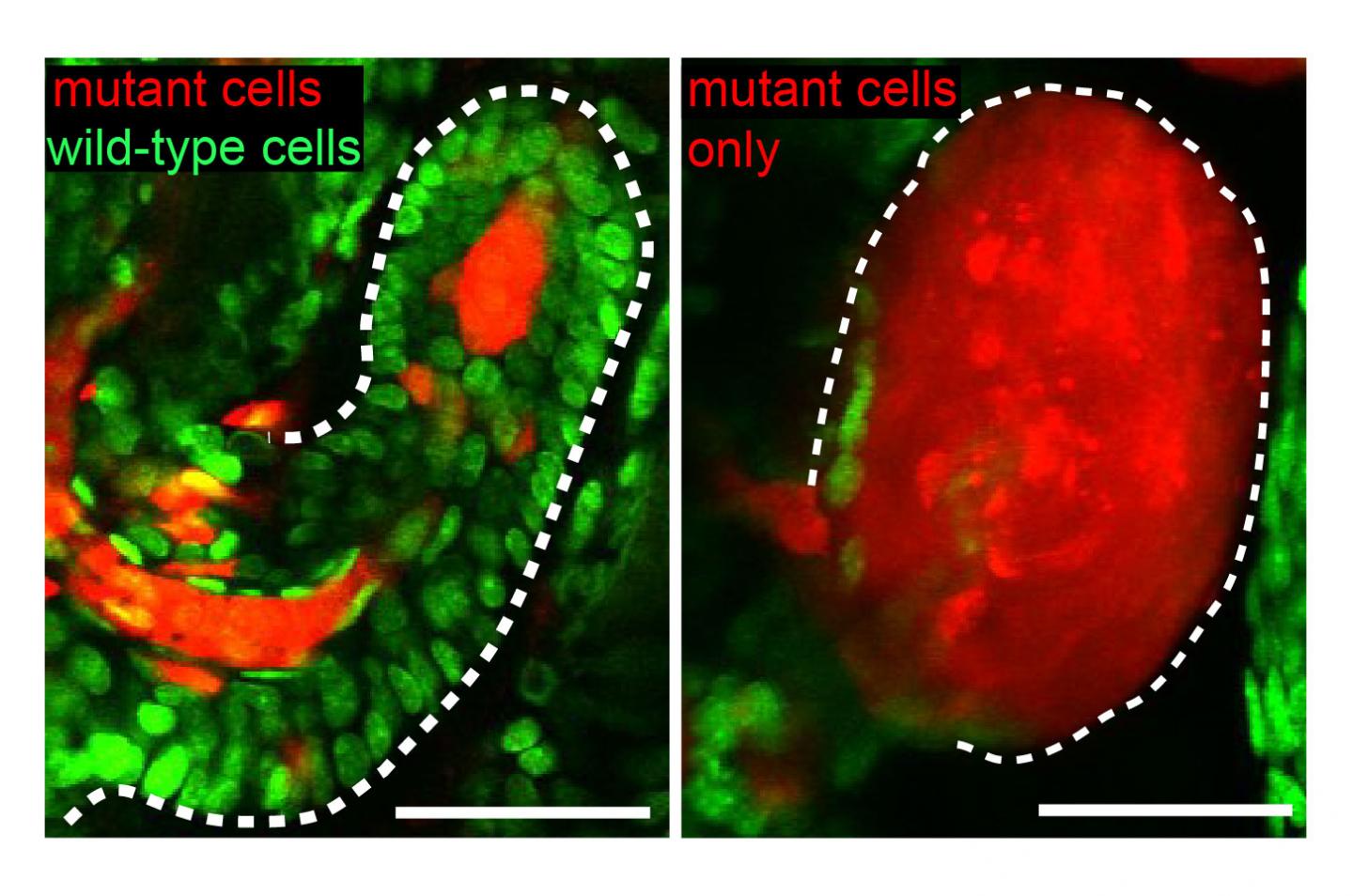
When Yale researchers took a closer look at skin cells, they discovered the unaffected neighbor cells are not helplessly awaiting invasion of cancer cells but acting like cellular police, actively correcting tissue flaws created by their aberrant neighbors, the investigators report Aug. 2 in the journal Nature.
"The normal cells can even corral and escort mutant cells out of the tissue and clean up the mess the mutant cells left behind, in order to keep the tissue healthy and functional," said Samara Brown. She and fellow graduate student Cristiana Pineda are lead authors of the study.
"We found a dynamic, active process of correction conserved across different mutational systems and even a mutation-independent model," Pineda added.
The Yale team studied damaged cells or activated oncogenes in mouse tissue and used new live-imaging technology to study behavior of surrounding cells. They found these wild-type cells were necessary for the elimination of tumors, which progressed dramatically in their absence, and for correcting aberrations caused by damaged cells.
Primary funding for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health and New York Stem Cell Foundation.
Brown and Pineda work in the lab of senior author Valentina Greco, associate professor of genetics, cell biology, and dermatology.
###
Media Contact
Bill Hathaway
[email protected]
203-432-1322
@yale
http://www.yale.edu
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature23304.