Credit: Kobe University
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) is known as "good" cholesterol, because HDL particles removes excess cholesterol from arterial walls and transport them back to the liver. A research group has developed a practical test for the ability of HDL to accept cholesterol. This method could help to prevent and monitor cardiovascular disease, and it is simple enough to be used in everyday clinical situations.
The group members include Senior Researcher HARADA Amane (Central Research Laboratories, Sysmex Corporation), Project Associate Professor TOH Ryuji (Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Division of Evidence-Based Laboratory Medicine) in collaboration with a research team led by Professor HIRATA Ken-ichi (Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine). The findings were published on May 31 in the online edition of The Journal of Applied Laboratory Medicine: An AACC Publication.
Standard health checks measure HDL-C, the amount of cholesterol collected by HDL – they do not look at HDL's capacity to accept cholesterol. However, HDL's ability to extract and accept excess cholesterol that has accumulated in cells is a more effective marker in preventing and monitoring cardiovascular disease.
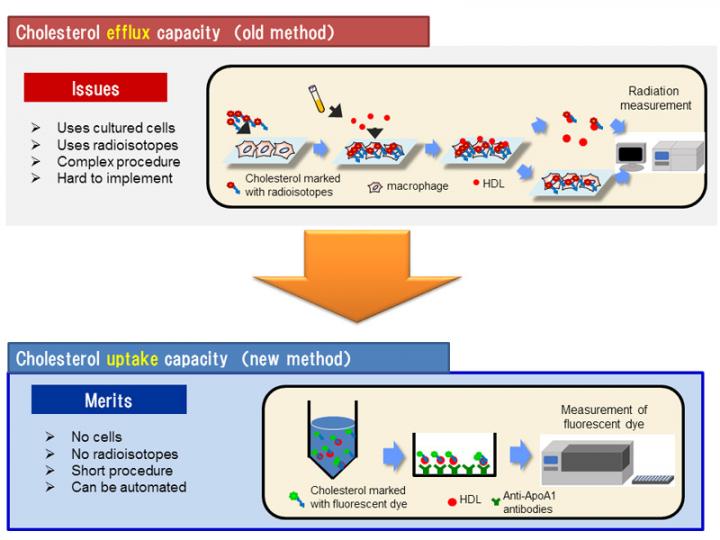
In order to measure HDL's ability to extract cholesterol (efflux capacity), standard methods use cultured cells that contain cholesterol marked by radioisotopes. This procedure is complicated and takes several days, so it cannot be used in everyday clinical situations. In this study, researchers invented a simpler and faster way to measure HDL capacity.
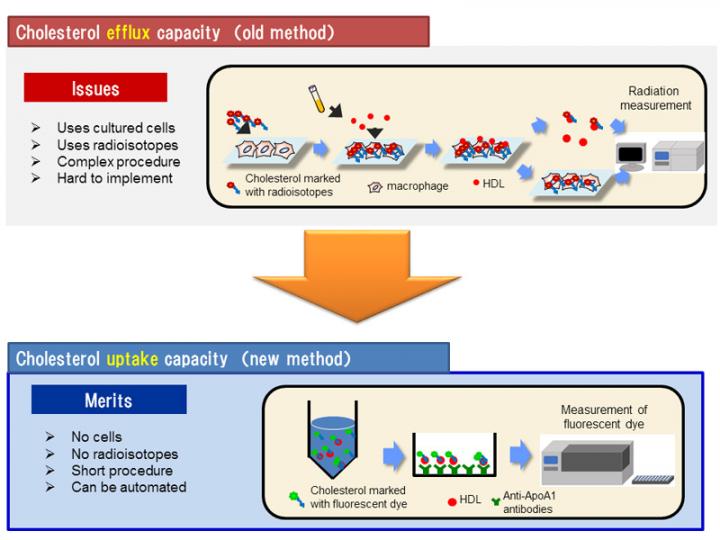
The team marked cholesterol with fluorescent dye instead of radioactive isotopes and added it to blood serum samples from test subjects. They supplemented the HDL in the blood serum and evaluated the amount of cholesterol accepted by HDL by measuring the strength of the fluorescence (figure 1). The team called the marker for this method cholesterol "uptake capacity", as opposed to the conventional method that measures cholesterol "extraction" (efflux) capacity.
The "uptake capacity" for cholesterol can be measured with a short processing time (within 6 hours), and is highly reproducible. It also shows good correlation with the conventional "extraction" capacity for cholesterol (figure 2). The study proved that this marker can be used to prevent and monitor cardiovascular conditions with the same effectiveness as the conventional method. The team also clarified that the uptake capacity for cholesterol had fallen in patients with cardiovascular disease (figure 3). They confirmed that this marker is a negative risk factor independent of bad cholesterol (LDL) and good cholesterol (HDL) (figure 3).
The research team is currently using this marker on a larger population to confirm the effect of decreased HDL capacity on the prevention and control of cardiovascular disease. The results of this study could help in creating strong core technology to develop drugs that improve HDL's function.
###
Media Contact
Eleanor Wyllie
[email protected]
@KobeU_Global
http://www.kobe-u.ac.jp/en/
Original Source
http://www.kobe-u.ac.jp/research_at_kobe_en/NEWS/news/2017_07_10_01.html http://dx.doi.org/10.1373/jalm.2016.022913