Credit: Yang Liu
Regular meteorological observations in most of China only started in the 1950s, meaning it is therefore necessary to reconstruct regional temperature series from high-resolution temperature proxies to compensate for the deficiency.
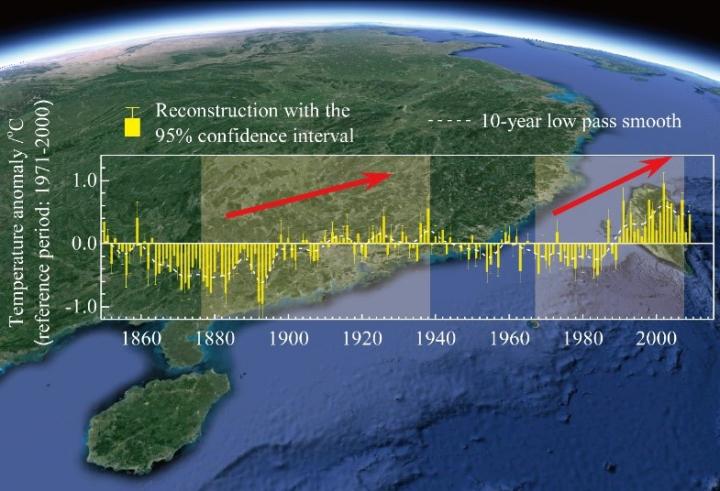
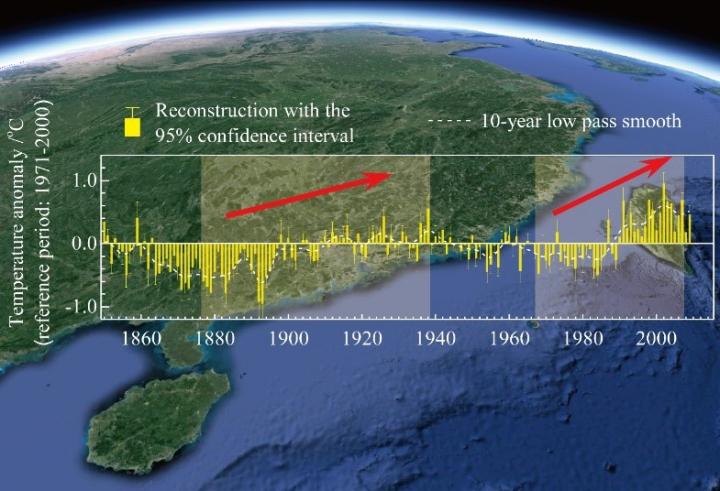
Scientists from the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, reconstructed the annual temperature anomaly in southern China during 1850-2009 based on the southern limit of snowfall recorded in Chinese documents, chronologies of tree-ring width, and tree-ring stable oxygen isotope (δ18O), using the method of signal decomposition and synthesis. The reconstructed series captures 65.8% of the variance of observations during 1952-2009, and the variance contributions of different frequency domains for the result is closer to those of temperature observations than reconstruction from a single proxy.
This multi-proxy-based temperature reconstruction shows robust centennial warming, with a linear trend of 0.47°C (100 yr)-1 during 1871-2009. Moreover, on the decadal scale, it shows the first rapid cooling as having started from the 1860s, followed by a cold interval until the early 1890s, with the coldest years being 1892 and 1893. The first significant warming is from 1877 to 1938 [0.125°C (10 yr)-1], with the most rapid rate of increase being 0.308°C (10 yr)-1 during 1892-1916, resulting in a moderate warm interval during the 1910s-1930s. Then, a slight temperature decline is apparent from the 1940s to the late 1960s. Another significant increase in temperature is shown to start around 1970 [0.258°C (10 yr)-1 during 1968-2007], with the highest rate being 0.512°C (10 yr)-1 during 1983-2002, though a warming hiatus occurs in the 2000s. Compared with the warm interval in the 1910s-1930s, the temperature in the 1980s-2000s is much higher. These results reveal that both the level of warmth and the warming rate from the 1980s are unprecedented since 1850.
This work, published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, provides an independent case to validate the global warming of the past 160 years and its recent hiatus.
###
Media Contact
Zheng Lin
[email protected]
86-108-299-5053
@aasjournal
http://english.iap.cas.cn/
Original Source
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00376-017-6228-x http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00376-017-6228-x
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag