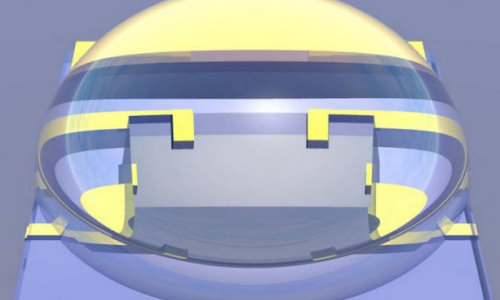
Researchers at IBM has given the transistor a major makeover, and it may enable the company to build computers that function more like the way the human brain works.
Photo Credits: New York Times
If it pans out, IBM could use the technology to build chips that are highly efficient and use much less electrical power. That could lead to a revolution in mobile devices, which today are bound by short battery lives and electrical inefficiency. The whole process is not unlike the charged electrical fluids sloshing around in our brains. If the brain can do it, an artificially crafted material might be able to do it too.
The new technology is based on materials called “correlated electron oxides,” which can be combined with an ionic liquid, or a mixture where half of the molecules carry a positive charge and half are negative. When you apply a tiny ionic voltage to the liquid, the charged particles move to opposite sides of the surface of the oxide material. The charge leaves the oxide and goes into the liquid, changing its conductive state from an insulator to a metal, or from something that does not conduct electricity to something that does.
And it maintains its electrical state until another charge is applied. That part of the research is new and is particularly encouraging. IBM believes it can create non-volatile memory, or chips that save data whether electricity is on or off. It can also make logic chips that would use less power than today’s silicon-based semiconductor chips, which are the brains of everything electronic.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by New York Times.