Credit: LIU Changmei
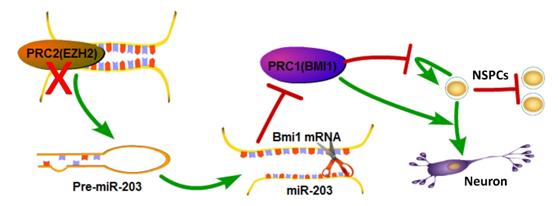
Polycomb group (PcG) proteins comprise the Polycomb complexes PRC1 and PRC2 that regulate gene expression levels through histone modification. Although PRC1 and PRC2 are emerging as having important roles in cancer stem cells, their functions in neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs) are largely unknown.
In a recent study published in Stem Cell Reports, a team led by Drs. LIU Changmei and TENG Zhaoqian from the State Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Reproductive Biology, Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, found a novel epigenetic signaling axis (composed of PRC1, microRNA, and PRC2) that regulates self-renewal and proliferation of NSPCs.
The researchers generated an Ezh2 (a key PRC2 component) conditional knockout mouse model, and found that Ezh2 loss of function results in decreased self-renewal and proliferation ability in NSPCs.
They then discovered that Ezh2 represses the expression of miR-203, which negatively regulates self-renewal and proliferation of NSPCs, but promotes their neuronal differentiation capacity.
In addition, they demonstrated that Bmi1 (a PRC1 component) is a direct downstream target of miR-203, and ectopic overexpression of BMI1 can rescue the self-renewal and proliferation deficiency exhibited by miR-203 overexpression in NSPCs.
As PcG proteins and microRNAs are usually co-expressed, these findings might have significant implications for other cell types or cancer tissues.
###
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation of China, National Science and Technology Major Projects, the State Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Reproductive Biology, and the Hundred Talents Program of CAS.
Media Contact
LIU Changmei
[email protected]
http://english.cas.cn/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.05.007
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag